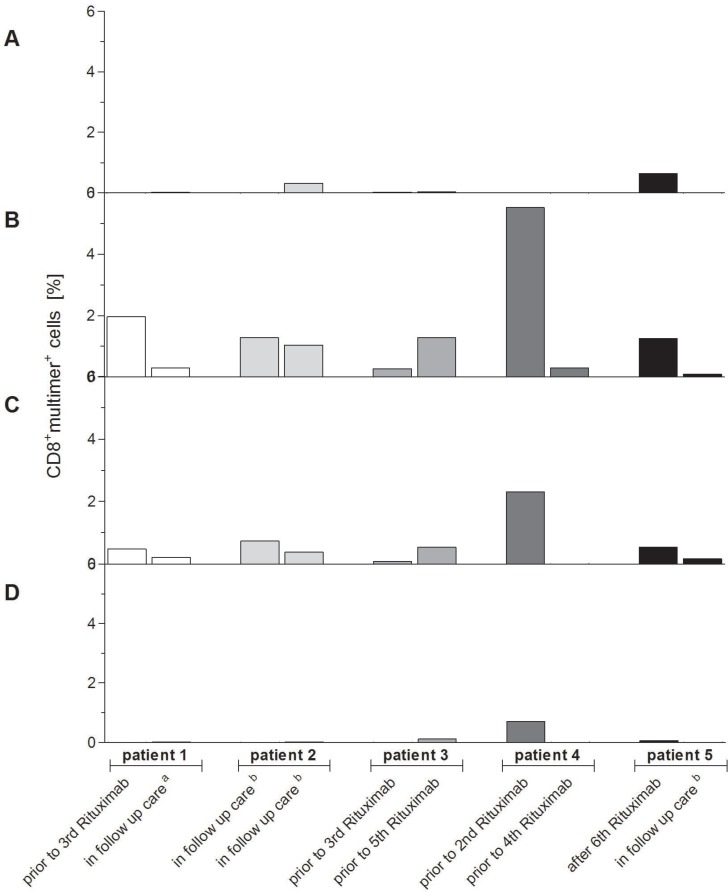
Figure 7.
(A–D) Verification of clinical relevance of the newly identified highly immunodominant CTL epitopes for EBV-associated PTLD. The clinical relevance of the highly immunodominant EBV-derived peptides (A*03_BILF2VTLA, A*03_BcRF1FLLA, A*03_BALF3QVAT) and the known immunodominant EBV-derived peptide (A*03_EBNA3ARLRA) for EBV-associated PTLD was verified by pMHC multimer staining and analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry. The respective frequencies of peptide-specific CD8+multimer+ T cells in HLA-A*03:01-positive patients suffering from EBV-associated PTLD were visualized by separately displaying the detected frequencies at two different points of time in the course of their treatment (n = 5). In order to exclude false-positive cells due to unspecific background level the general nonsense was applied and its respective percent value was subtracted from the patients’ frequencies specific to one of the peptides. At the time of blood withdrawal patients were prior to receiving their second, third, fourth or fifth treatment with rituximab, after their sixth treatment with rituximab, in follow-up care ensuing cytotoxic chemotherapy (a) or in follow-up care subsequent to no other treatment than rituximab (b). The resultant precursor frequencies of peptide-specific CD8+multimer+ T cells are shown as follows: (A) A*03_EBNA3ARLRA, (B) A*03_BILF2VTLA, (C) A*03_BcRF1FLLA and (D) A*03_BALF3QVAT.