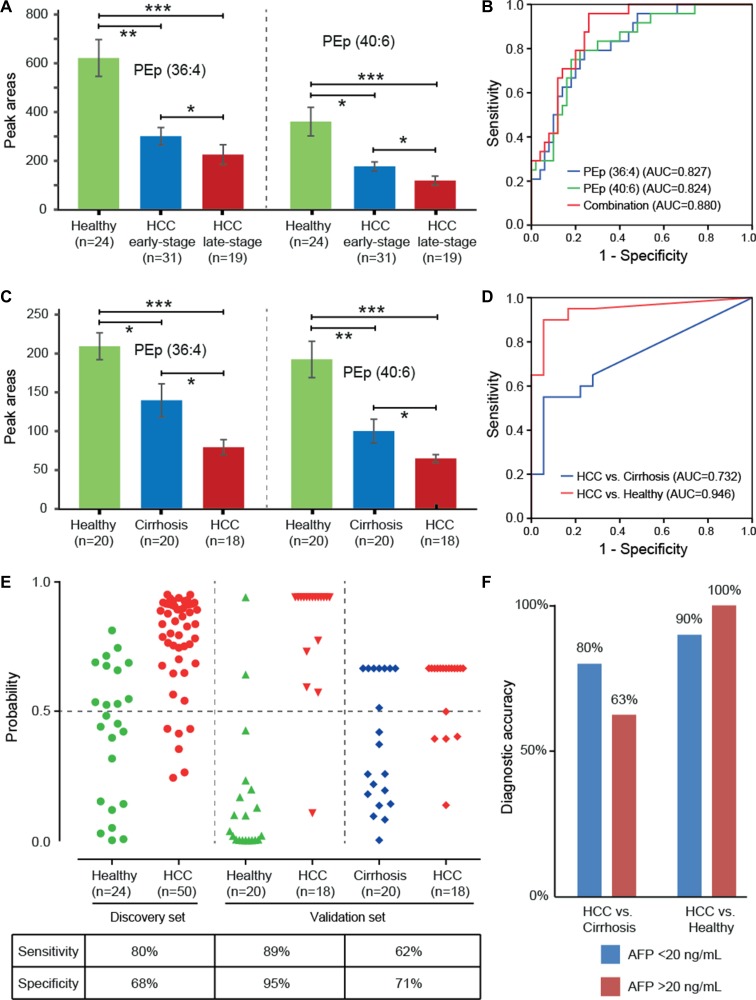
Figure 2. Diagnostic capabilities of PEp (36:4) and (40:6) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
(A) Altered expressions of PEp (36:4) and (40:6) in serum of healthy subjects, early-stage HCC patients, and late-stage HCC patients; (B) ROC curve of serum PEp (36:4) and (40:6) in the discovery set; (C) Altered expressions of PEp (36:4) and (40:6) in serum of healthy subjects, liver cirrhosis patients, and HCC patients; (D) ROC curve of the combination of PEp (36:4) and (40:6) in the validation set; (E) Discrimination of healthy subjects, liver cirrhosis patients, and HCC patients by using the combined serum levels of PEp (36:4) and (40:6), at a cut-off of probability of 0.5; (F) Diagnostic accuracy of the combined marker PEp (36:4) and (40:6) for HCC patients with different concentrations of AFP in the validation set.