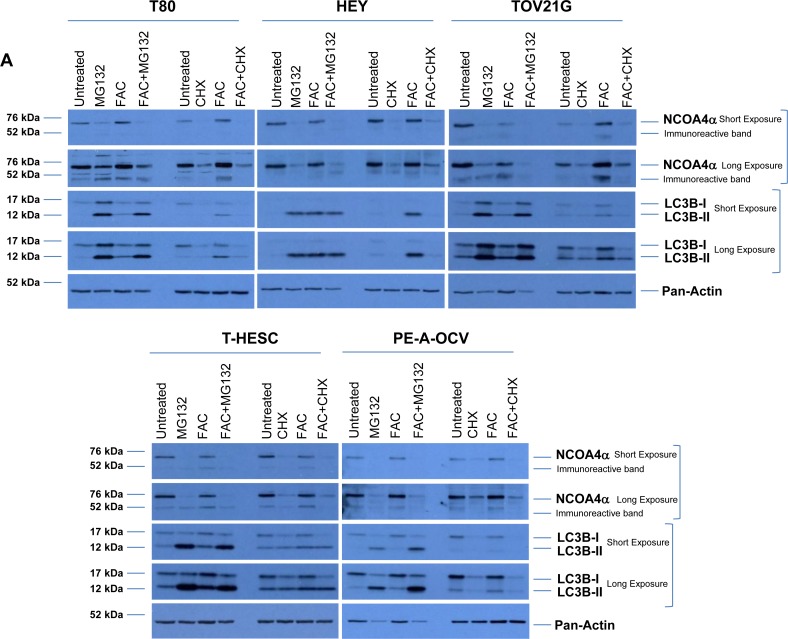
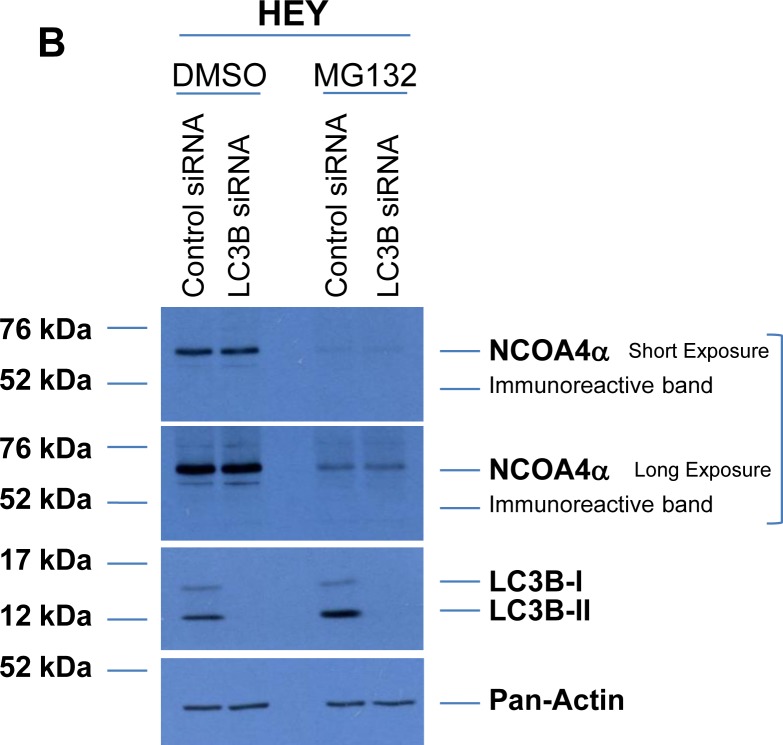
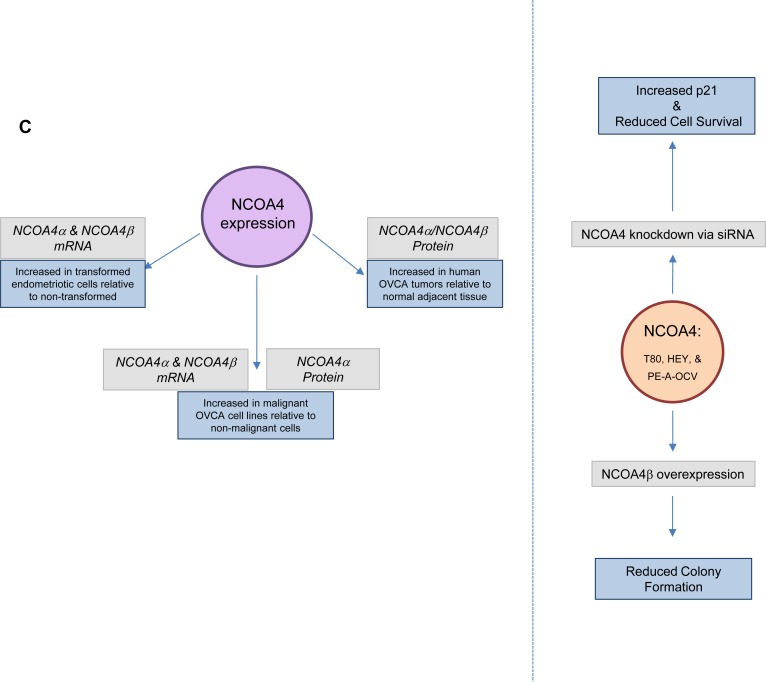
Figure 7. NCOA4 protein is regulated in a proteasome- and autophagy-independent manner.
(A) Cell lysates from untreated T80, HEY, TOV21G, T-HESC, and PE-A-OCV or cells treated for 18 hours with 5 μM MG132, 2 μg/ml CHX, 250 μM FAC or a combination of MG132 with FAC or CHX with FAC were analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Data shown is representative across three independent experiments. (B) Cell lysates from non-targeting control or LC3B siRNA transfected HEY cells treated in the absence or presence of 5 μM MG132 were analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Data shown is representative across three independent experiments. (C) Schematic summarizing the results presented herein. mRNA expression of NCOA4α and NCOA4β are increased in transformed endometriotic cells (compared to non-transformed controls) and malignant OVCA cell lines (compared to non-malignant gynecological cell lines). NCOA4α protein is increased in malignant OVCA cell lines (compared to non-malignant gynecological cell lines). In addition, total NCOA4 protein was increased in a subset of human OVCA tumors (compared to normal adjacent tissues). Modulation of NCOA4 expression in T80, HEY, and PE-A-OCV cells led to changes in cellular survival.