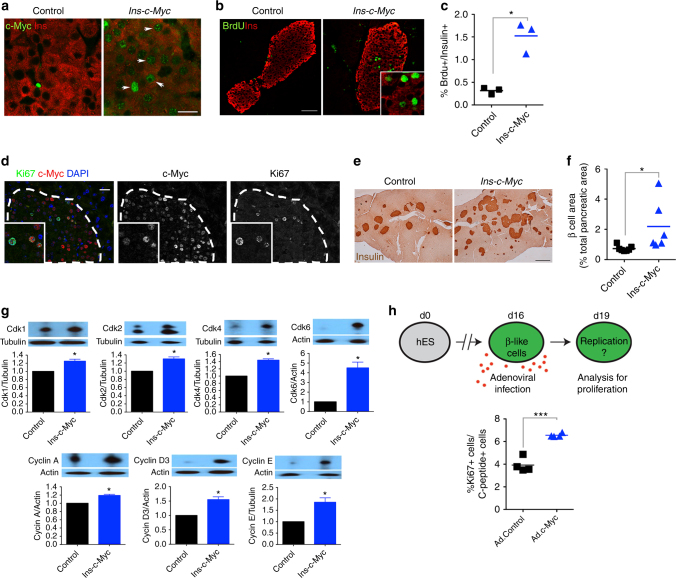
Fig. 2.
c-Myc stabilization increases β-cell replication. a Nuclear accumulation of c-Myc (green) in transgenic β cells (Insulin, red). Scale bar, 15 μm. Image shown is representative of at least three biological replicates. b BrdU (green) staining in Ins-c-Myc β cells (Insulin, red). Scale bar, 50 μm. c Quantification of BrdU incorporation in Ins-c-Myc animals (n = 3) as compared to controls (n = 3). *p < 0.05, Student’s t test. d c-Myc expressing β cells co-stained with Ki67 in transgenic mice. Scale bar, 20 μm. Insulin staining (e) and islet mass quantification (f) in Ins-c-Myc mice (n = 6) as compared to controls (n = 7). Scale bar, 100 μm. *p < 0.05, Student’s t test. g Quantification of the seven signature proteins in Ins-c-Myc islets. n = 3 per group, error bars indicate ± SD, *p < 0.05, Student’s t test. All animals were three months old and were not administered TAM. h Cartoon summarizing experimental approach to test the effect of c-Myc on proliferation of hESC-derived β-like cells. Adenoviral infection was used to deliver either control (Ad. Control) or c-Myc (Ad.c-Myc) to hESC-derived β-like cells, and Ki67 staining quantified. n = 4. ***p < 0.0005, Student’s t test