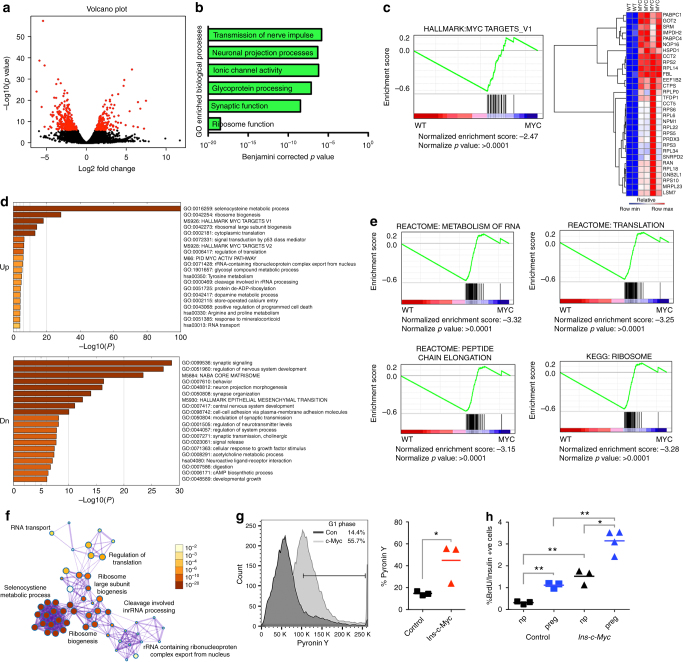
Fig. 5.
Global changes in β cells with stabilized c-Myc lead to an immature phenotype. a Volcano plot of transgenic (Ins-c-Myc) islets as compared to controls, with genes that are significantly (p value < 1e−06) changed marked in red. b Gene ontology analysis shows significant changes in cell growth processes, with the most significant change in “Ribosome Function” in transgenic islets. c Hallmark c-Myc targets that were highly significantly enriched in the transgenic samples identified using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). d Pathways differentially upregulated or downregulated in transgenic islets as compared to controls. e GSEA analysis of differentially expressed genes shows enrichment of genes involved in RNA and protein synthesis in the transgenic (myc) samples as compared to the controls (WT). f Metascape analysis shows significant overlap between RNA and protein synthesis pathways in the transgenic islet samples. Color-coding denotes p values. g Pyronin Y staining of islets isolated from Ins-c-Myc and control animals. n = 3 per group. *p < 0.05, Student’s t test. h BrdU incorporation was quantified in control (squares) and Ins-c-Myc (triangles) animals at 3 months of age either not pregnant (black) or at 14.5 days of gestation (blue). n = 3 per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, Student’s t test