Fig. 3.
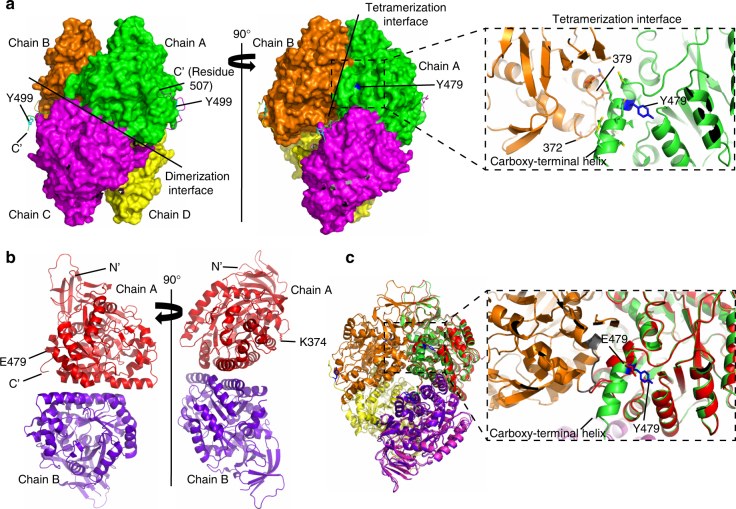
Phosphorylation of CRMP2 at Y479 induces oligomerization changes in CRMP2 structure. a (Left panel) Surface representation of a tetramer of CRMP2 (residues 13–516) showing the dimerization interface. Visible carboxy-terminal (C’) extensions of each chain are shown as ribbons. Reader-visible Y499 are labeled and shown in cyan. a (Right panel) Tetramerization interface between the dimers is shown. The position of Y479 at the interface is also highlighted in blue. Zoom-in shows the details of this interface comprising the carboxy-terminal helix of chain A and residues 372–379 of the neighboring chain B. b Crystal structure of the phosphomimetic mutant CRMP2–2E. (Left panel) Position of E479 is highlighted. (Right panel) Position of SUMOylation site, K374, is highlighted. c Superposition of CRMP2 wild-type tetramer structure and CRMP2–2E phosphomimetic mutant dimer structure. Zoom-in showing key differences at the tetramerization interface: chain A (green) of CRMP2 (residues 13–516) has the Y479 (blue) at the carboxy-terminal helix which interacts with the loop (gray) of chain B (orange). CRMP2–2E mutant (red) has E479 in the position. The mutation introduces a charge in the hydrophobic cavity, causing the carboxy-terminal helix to unwind and the tetramer to break