Fig. 4.
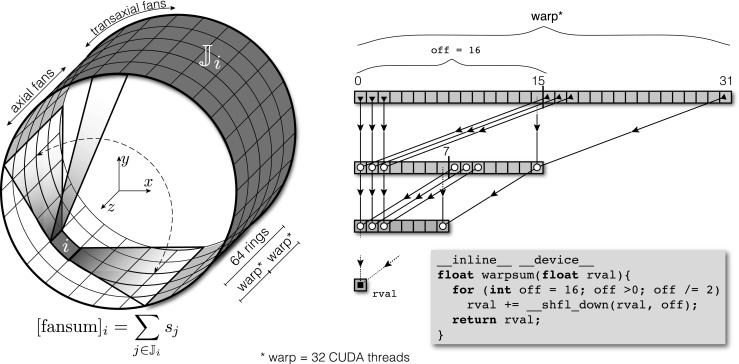
Calculation of 3D fan sums for each detector i: The sum is first calculated axially by forming axial fans of 64 rings and then transaxially by forming transaxial fans, such that all detectors in coincidence with detector i are summed (three axial fans are shown within the detector rings where two of the fans are on extreme ends). One axial fan sum is calculated by two CUDA warps (see the figure on the right), where each warp consists of 32 CUDA threads executed in parallel. The values stored in 32 registers (one register per thread) are reduced to one sum through fast parallel reductions obtained through rapid communications between the threads and facilitated by CUDA shuffle instructions (Luitjens 2014). The same is done for the other warp to form one axial fan sum. Repeating it over all transaxial detectors will constitute a full fan sum for detector i
