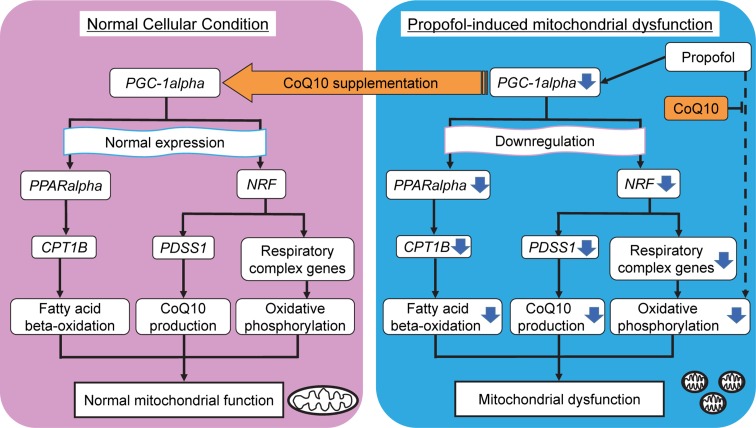
Fig. 6.
Model of propofol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and protective effects of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Mitochondrial dysfunction can be caused by propofol-induced downregulation of PGC-1-alpha and its downstream target genes associated with mitochondrial energy metabolism in cardiomyocytes. As an additional mechanism, propofol can take over the role of CoQ10 and inhibit oxidative phosphorylation directly in mitochondria. Co-treatment with CoQ10 can contribute to the maintenance of mitochondrial function through recovery of gene expression