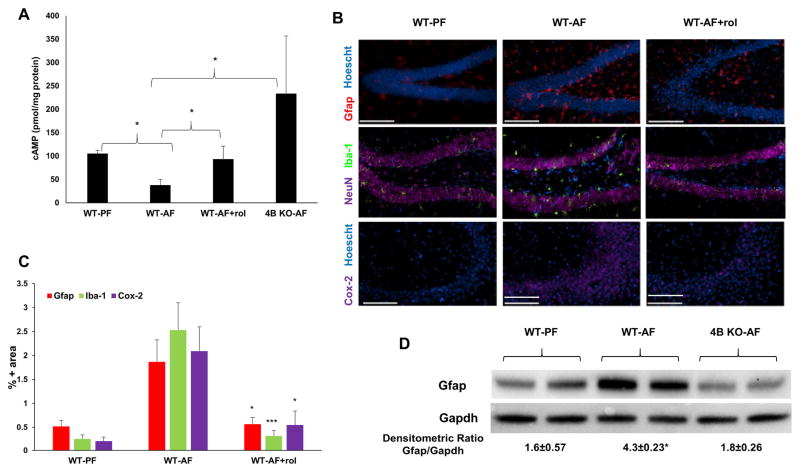
Figure 6.
Pde4 inhibition prevents alcohol-induced effects on cAMP and inflammation in the brain. A, Brains from PF and AF mice were lysed, and cellular cAMP levels were measured. Obtained cAMP values were normalized by protein content. Data are presented as means ± SD (n=5–7 in each group). *P < 0.05. B, Cox-2, Gfap and Iba-1 expression in mouse brains. Images are representative of the inflammatory state of the whole brain of their respective treatment groups. (n = 5–7 in each group). C, Quantitation of IHC staining. The percentage of image area positive for Gfap, Iba-1, and Cox-2 are significantly lower (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001) in rolipram-treated alcohol-fed mice (WT-AF+rol) relative to alcohol-fed animals (WT-AF). (n = 5–7 in each group). Bar = 100 μm. Data are means ± S.D. D, Immunoblot analysis of brain Gfap of WT and Pde4b−/− mice fed alcohol for 2 weeks. *p<0.05 compared to WT-PF and 4B KO-AF.