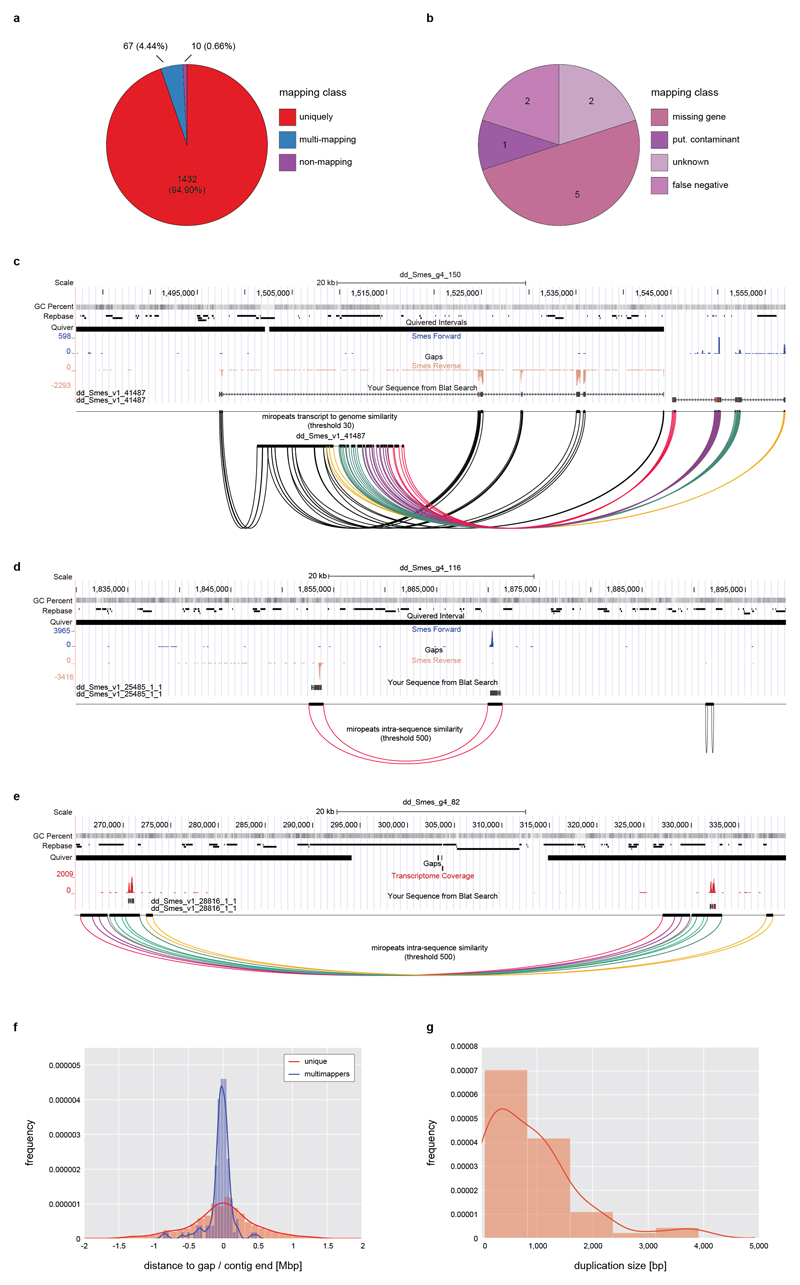
Extended Data Figure 2. Assembly validation by high stringency transcript back-mapping.
a) Quality control of the Smed assembly by means of high stringency back mapping of 1,509 high confidence (HC) cDNAs. HC-cDNAs were defined as having BLAST hits with > 90% query and subject coverage in 7 other planarian transcriptomes in PlanMine17. HC-cDNAs were mapped to the Smed assembly using > 90 % query coverage and sequence identity as cut-off criteria. The pie chart visualizes the absolute number and relative proportions of HC-cDNAs mapping with the indicated characteristics. b) Further analysis of the 10 HC-cDNAs classified as non-mapping from a) by intersection with the mapping results of Extended Data Fig. 1g. These 2 were designated as “false positive”, since both mapped to the Smed genome with > 90 % query coverage and sequence identity using BLAT. c) UCSC genome browser screenshot (75 kbp window) of the genomic mapping location of one of the two “unknown” HC-cDNAs as single example of a mapping failure due to an actual assembly error. The example documents inversion of the 5’-end of the cDNA within a low confidence stretch at a contig end (lack of coverage in the Quiver track). The inversion is supported by i) inverted RNAseq read mapping and ii) inversion of the cDNA sequence shown in the respective tracks. Below: Color-coded Miropeats similarity plots of respective regions. d), e) Examples of genomic mapping loci of HC-cDNA transcripts out of the multi-mapping category in a), browser screen shots as described in c). d) Example of a likely legitimate (biological) gene duplication in a gap-free high confidence region. e) Micro tandem duplication surrounding a scaffolding gap in a repeat rich region. f) Multi-mapping HC-cDNAs map preferentially to contig ends. The histogram graphs the distance of the closest gap or contig end for the 67 multi-mappers and a corresponding number of unique mappers a). g) Estimated size of the duplicated regions of multi-mapping HC-cDNAs. Jointly, this analysis identifies a small fraction of small-scale duplications at assembly gaps in the Smed assembly, which can be easily identified with the help of the various quality control tracks in the PlanMine genome browser.