FIG. 3.
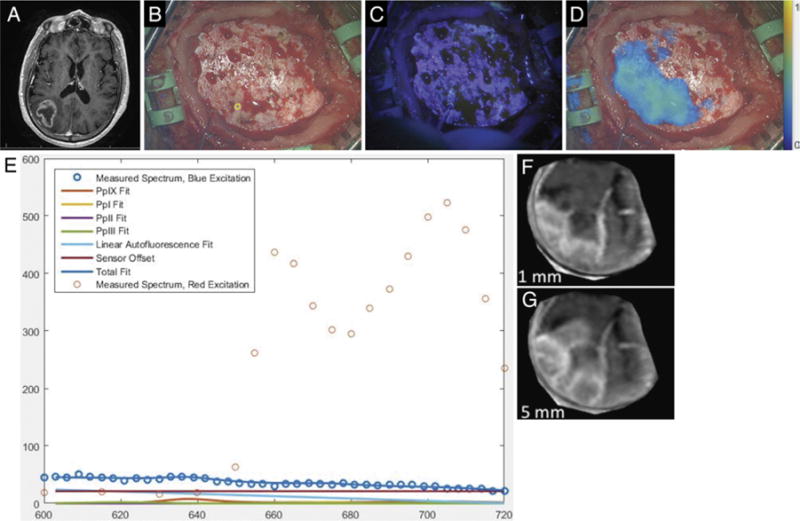
Case 3. A: Axial T1-weighted MR image showing a right parietal tumor. B: Under white-light visualization, the intact and normal-appearing dura has been exposed upon elevation of the free bone flap. (The small yellow circle in the lower middle portion of the figure corresponds to the site of handheld optical probe measurements, whose spectra are shown in panel E.) C: Under blue-light excitation, no red fluorescence is visible. D: Under red-light excitation, fluorescence (650–720 nm) corresponding to underlying tumor was detected and is displayed in a false color overlaid on the white-light image. E: The optical spectra acquired with the handheld optical probe and corresponding model fits for PpIX, photoproducts, and autofluorescence at the site indicated by the small yellow circle in panel B. The typical red emission peak of PpIX at 635 nm under blue-light excitation is absent, while emission at longer wavelengths is detected under red-light excitation, confirming the presence of PpIX. F: Reconstruction of weighted MRI data corresponding to a plane 0–1 mm below the dural surface in the operative field. G: Reconstruction of weighted MRI data corresponding to a plane 0–5 mm below the dural surface in the operative field.
