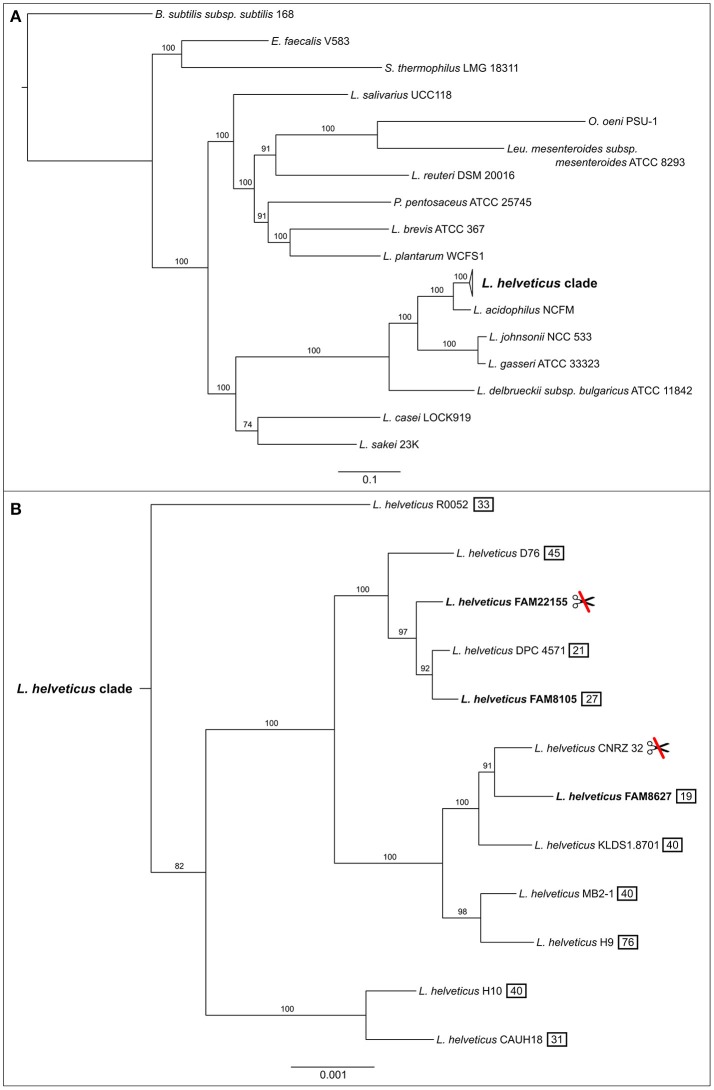
Figure 4.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of completely sequenced L. helveticus strains, in the context of several key LAB strains. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using a concatenated alignment of 107 known housekeeping genes (Dupont et al., 2012). (A) The collapsed L. helveticus clade relative to other LAB bacteria. Bootstrap scores for all nodes are shown (percentage of 100 bootstrap runs). The bar at the bottom represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis 168 served as outgroup. (B) Expanded L. helveticus clade based on the same calculation as above. The three strains of this study are shown in bold. The L. helveticus clade has a 100 times higher resolution than the complete tree which is reflected by the bar. The symbol showing crossed scissors indicates two strains without a CRISPR/Cas system; the numbers in a black box indicate how many CRISPR spacers were detected in total per strain.