Figure 2.
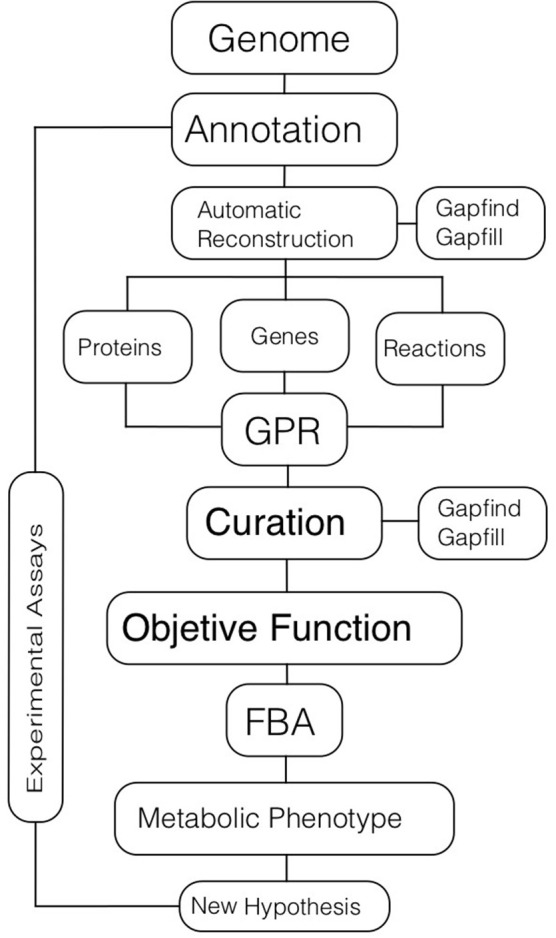
Metabolic modeling. The process of metabolic modeling starts with a genome annotation used for inferring metabolic reactions that are present in an organism. Automatic tools could be used for reconstructing the metabolic network based on the genome. In the initial set of reactions there will be metabolic gaps or missing reactions that are necessary for the complete function of pathways. These gaps can be identified and filled out using different algorithms. The final metabolic reconstruction will have associations among genes, proteins, and reactions (GPRs). Then, further manual curation, based on omics data and literature should be performed. The definition of an objective function that represents a target biological function to optimize should be defined, typically cell growth or ATP production. Once the objective function is set, computational simulations for obtaining metabolic phenotypes related to different conditions are carried out; Flux Balance Analysis (FBA) is the main technique for these simulations. Finally, new biological hypotheses are generated and validated. In all the procedure, data, and information from different experimental assays are incorporated into the model.
