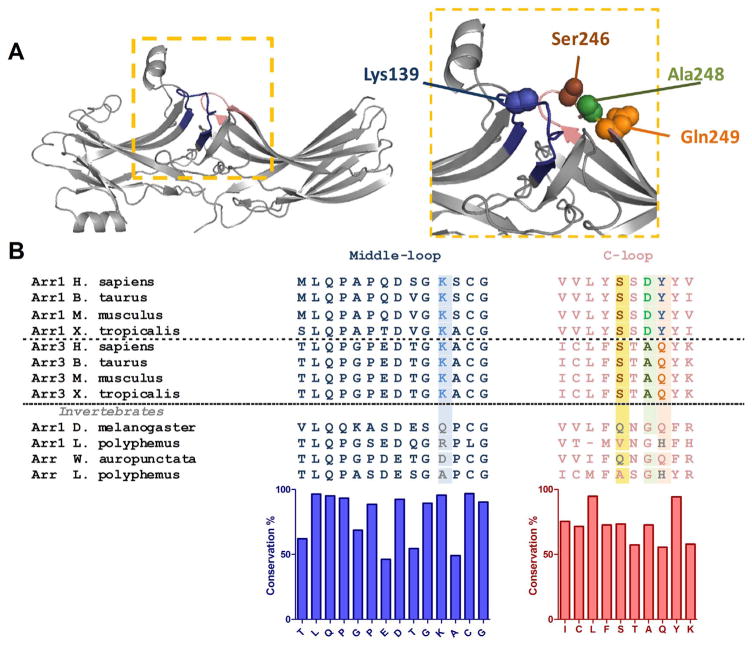
Fig. 1.
Structure and sequence of the middle and C-loops of arrestins. A. Crystal structure of rhodopsin-bound arrestin-1 (Protein Data Bank entry 4ZWJ [27] ). The middle and C-loops are shown in blue and pink, respectively. Residues mutated in this study are shown as CPK models. B. Multiple sequence alignment of arrestin-1 (Arr1), arrestin-3 (Arr3) and arrestin homologs (Arr) from invertebrate species. Residues mutated in this study are highlighted. Bar graph under the alignment shows the extent of residue conservation at each position. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)