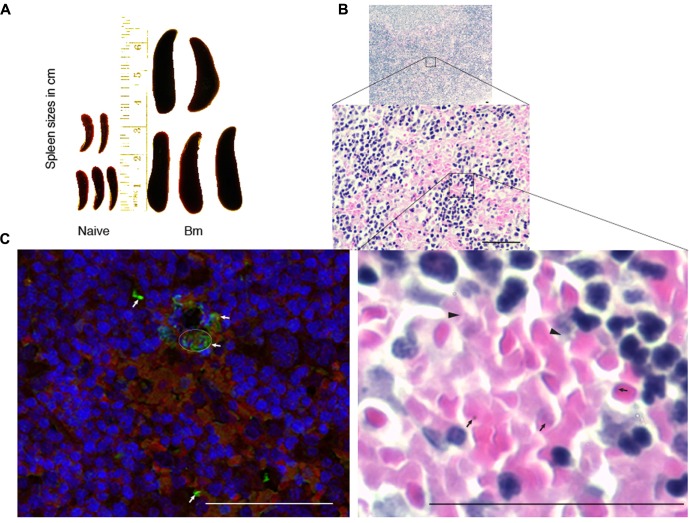
FIGURE 3.
Impact of B. microti infection on spleen of the infected mice. (A) B. microti infection resulted in a significant increase in spleen sizes of mice compared to uninfected, naïve mice. (B) White and red pulp zones were significantly enlarged while demarcation zone was not apparent in the spleen of B. microti infected mice. Numbers of lysed erythrocytes (marked by arrowheads) as well as various free parasitic forms (marked by arrows) were also observed in infected mouse spleen. (C) In IFA conducted the spleen section, red color indicates auto-fluorescence of RBCs, blue shows nuclear staining of cells while green fluorescence marks B. microti probed with infected human plasma followed by detection with Alexa fluor 488 conjugated secondary antibodies. Apparent lysed infected erythrocytes presence is marked by a circle. Several free, released parasitic forms were also detected (marked by arrows) among erythrocytes. Bars represent 25 μm.