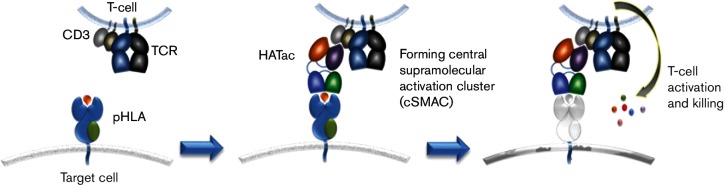
Fig. 1.
Action of the HATac. The target cell, such as an HCV-infected cell, is bound by HAT fused with an anti-CD3 scFv partner that can bind to T cells possessing any specificity, for example, CMV-specific CD8+ T cells for overcoming HCV-specific T-cell exhaustion. Such interaction might form a stable cSMAC, which would result in CMV-specific T-cell activation to kill the HCV-infected target cell.