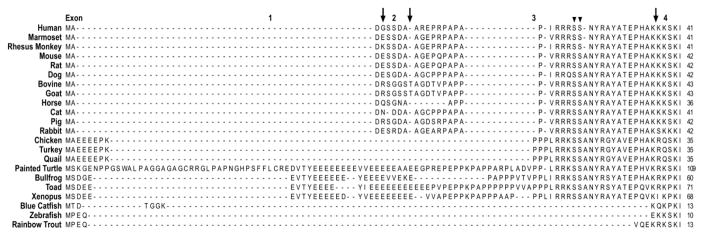
Figure 2.
Amino acid sequence alignment of the N-terminal extension of vertebrate cTnI was performed with the MegAlign computer program (Lasergene; DNASTAR, Inc, Madison, WI) using the Clustal V method. The sequence alignment demonstrated that the N-terminal extension of mammalian cTnI is highly conserved, whereas it shows notable sequence variations in avian, reptile and amphibian species, and is absent in fish cTnI. The three arrows indicate the exon boundaries based on the structure of human TNNI3 gene. The two arrowheads indicate the two PKA phosphorylated Ser residues. The NCBI database accession numbers for the protein sequences analyzed are the same as that for Fig. 1.