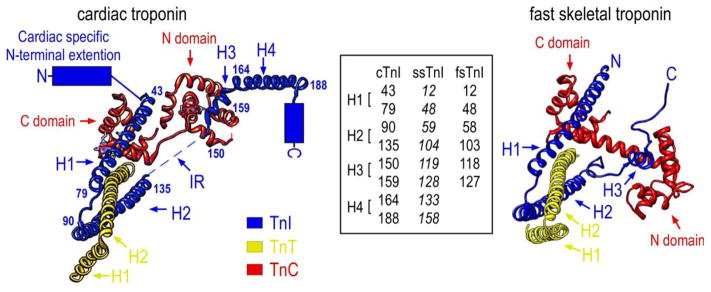
Figure 3.
The left schematic structure illustrates the position of cTnI in the crystal structure of the troponin complex and its interactions with TnC and the partial structure of TnT in the Ca2+-saturated state (PDB 1J1E) (Takeda et al., 2003). The four α-helices are indicated: H1 (43–79), H2 (90–135), H3 (150–159), H4 (164–188). The counterpart residues in ssTnI and fsTnI were shown in the inset box to denote the helix boundaries. As there is no crystal structure available for ssTnI, the helix boundaries (in Italic font) in ssTnI are deduced from protein sequence alignment with cardiac and fast skeletal muscle TnI. No high resolution structure of the N-terminal extension, the C-terminal end segment and the inhibitory region (IR) were resolved for human cardiac troponin. The right schematic crystal structure of chicken fast skeletal troponin (PDB 1YTZ) (Vinogradova et al., 2005) showed only three α-helices (H1, H2 and H3) in fsTnI but included the inhibitory region. The C-terminal end segment of fsTnI is disordered in the crystal structure of chicken fast skeletal muscle troponin complex when Ca2+ is bound.