Figure 1. Effect of BCG viability on iNOS mRNA Expression and NO production.
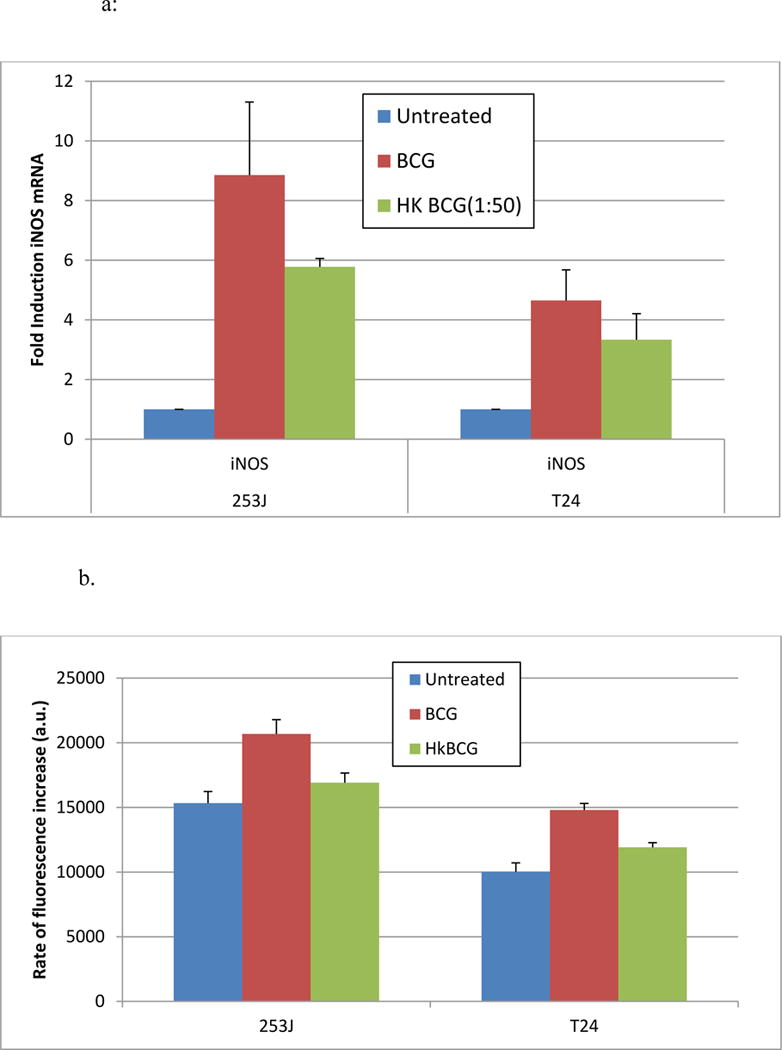
Exposure of UC cells to viable BCG increased the expression of iNOS mRNA 8.8- and 4.6-fold in 253J and T24 cells, respectively. This increase was reduced to 5.8- and 3.3-fold in response to hk BCG. The difference in iNOS induction between viable and hkBCG was not statistically significant (p = 0.15).
Exposure of UC cells to BCG significantly increased NO production in both cell lines (p < 0.05). Relative to controls, BCG treatment significantly increased NO levels in both T24 (p < 0.0001) and 253J cell lines (p < 0.05). Treatment with hk BCG significantly increased NO levels in T24 p < 0.05) but not in 253J p= 0.4). The difference in NO production between hk BCG and BCG was statistically significant (p < 0.05).
