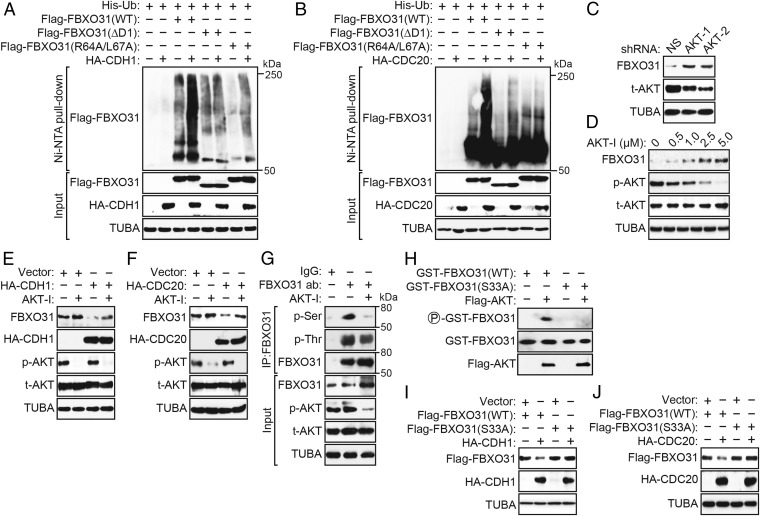
Fig. 3.
Polyubiquitination of FBXO31 by CDH1 or CDC20 is dependent on phosphorylation by AKT kinase. (A and B) In vivo ubiquitination assay. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing His-ubiquitin, Flag-FBXO31(WT), Flag-FBXO31(ΔD1), or Flag-FBXO31(R64A/L67A) and HA-CDH1 (A) or HA-CDC20 (B). Proteins bound to His-ubiquitin were purified by Ni-NTA pull-down, washed, and eluted in imidazole. Ubiquitinated Flag-FBXO31 was detected using an anti-Flag antibody. (C) Immunoblot monitoring the levels of FBXO31 and total AKT (t-AKT) in HEK293T cells expressing a NS shRNA or one of two unrelated AKT shRNAs. (D) Immunoblot monitoring FBXO31, phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT), and t-AKT in HEK293T cells treated with various concentrations of AKT inhibitor (AKT-I). (E and F) Immunoblot monitoring endogenous FBXO31 in HEK293T cells expressing HA-CDH1 (E) or HA-CDC20 (F) in the presence or the absence of AKT-I. (G) Coimmunoprecipitation monitoring the presence of phosphorylated Ser (p-Ser) or phosphorylated Thr (p-Thr) in the FBXO31 immunoprecipitate from HEK293T cells treated in the presence or the absence of AKT-I. (H) In vitro kinase assay monitoring the ability of purified AKT to phosphorylate GST-FBXO31(WT) or GST-FBXO31(S33A). (I and J) Immunoblot monitoring levels of Flag-FBXO31(WT) or Flag-FBXO31(S33A) in HEK293T cells expressing vector, HA-CDH1 (I), or HA-CDC20 (J).