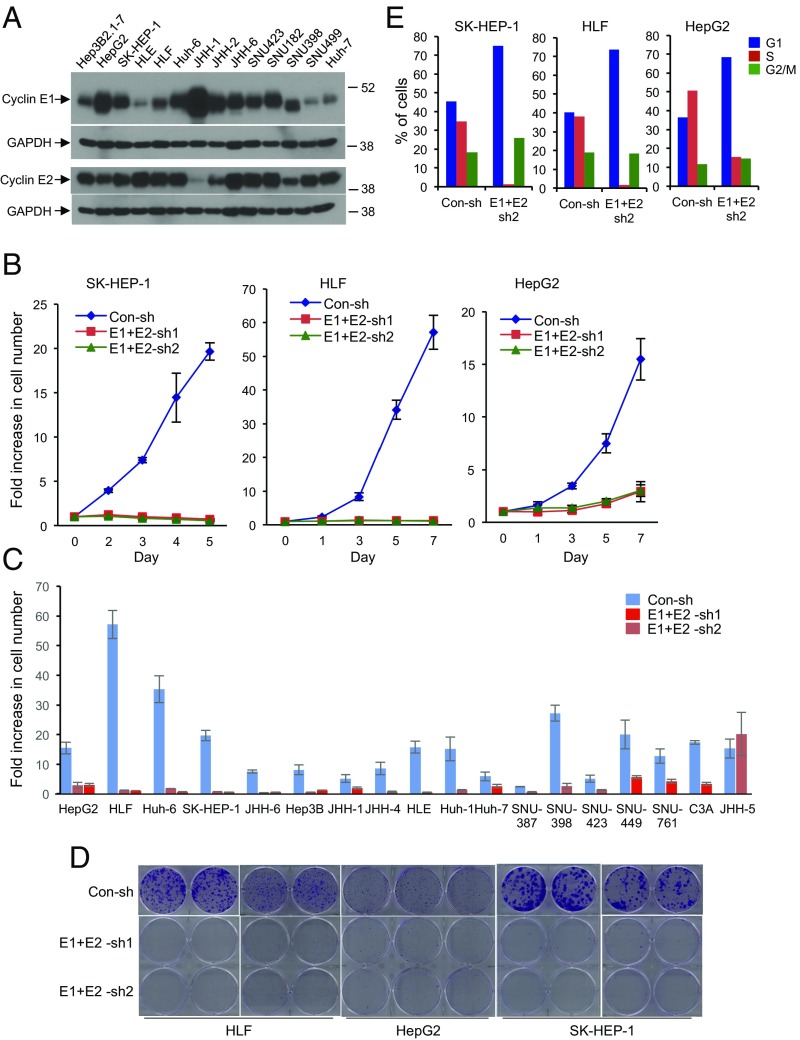
Fig. 2.
E-type cyclins are required for human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation. (A) Western blot analysis of cyclin E1 and E2 levels in the indicated human HCC cell lines. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Growth curves of human HCC cell lines SK-HEP-1, HLF, and HepG2. Cells were transduced with viruses encoding two different sets of anti-cyclin E1 and E2 shRNAs (E1+E2-sh1, E1+E2-sh2), or control shRNA (Con-sh). Error bars indicate SD, n = 3. (C) Fold increase in cell numbers in the indicated 18 human HCC cell lines following depletion of cyclins E1 and E2. Cells were transduced as in B, plated, and the fold increase in cell number was measured 6–7 d after plating. Note that only in JHH-5 cells, the growth rate was not affected by depletion of cyclins E1 and E2. Error bars indicate SD, n = 3. (D) Clonogenicity assays of HLF, HepG2, and SK-HEP-1 cells following depletion of cyclins E1 and E2, as in B. (E) Cell cycle distribution of human HCC cell lines SK-HEP-1, HLF, and HepG2 following depletion of cyclins E1 and E2. Cells were pulsed with bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU), stained with an anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentages of cells in each cell cycle phase are indicated.