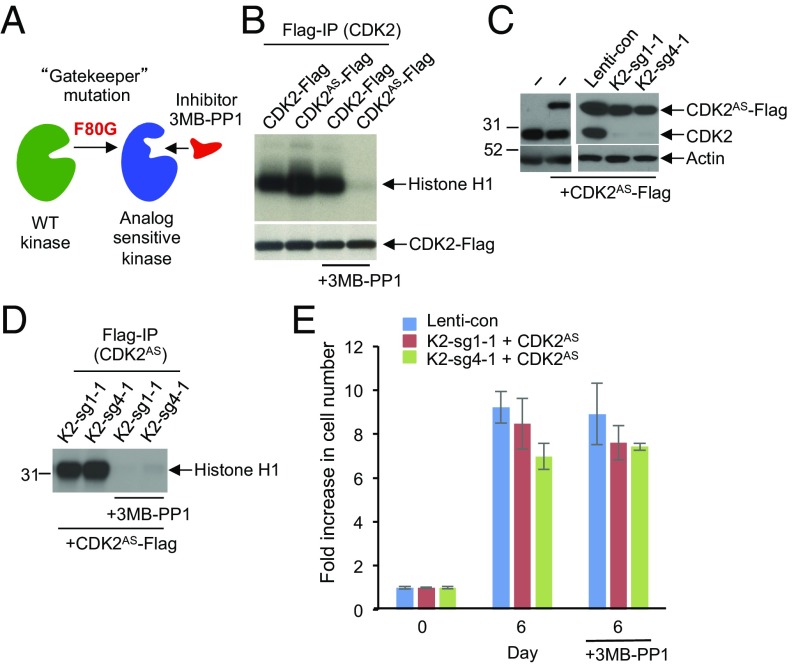
Fig. 5.
Analyses of HCC cells expressing analog-sensitive CDK2. (A) Diagram illustrating the principle of analog-sensitive kinases. (B) Flag-tagged wild-type or analog-sensitive CDK2 (CDK2AS) were ectopically expressed in 293T cells, immunoprecipitated, and subjected to in vitro kinase assays in the presence or absence of 1 μM 3MB-PP1. Note inhibition of the analog-sensitive CDK2 by 3MB-PP1. (C) Western blot analysis of the levels of ectopically expressed analog-sensitive CDK2 (CDK2AS-Flag) and the endogenous CDK2 (CDK2) in parental HepG2 cells (−), or HepG2 cells transduced with control lenti-viruses (Lenti-con), or in CDK2-knockout HepG2 cells (K2-sg1-1 and K2-sg4-1). Actin was used as loading control. (D) CDK2-knockout HepG2 cells (K2-sg1-1 and K2-sg4-1) were engineered to ectopically express Flag-tagged analog-sensitive CDK2 (+CDK2AS-Flag). CDK2AS was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody and used for in vitro kinase assays using histone H1 as a substrate. Note that treatment with 3MB-PP1 inhibited the catalytic activity of CDK2AS. (E) Cell growth of control HepG2 cells (Lenti-con) or CDK2-knockout HepG2 cells (K2-sg1-1 and K2-sg4-1) ectopically expressing analog-sensitive CDK2 (+CDK2AS). Cells were cultured in the presence or absence of 3MB-PP1, and fold increase in cell numbers was determined after 6 d. Shown are mean values, error bars indicate SD, n = 3.