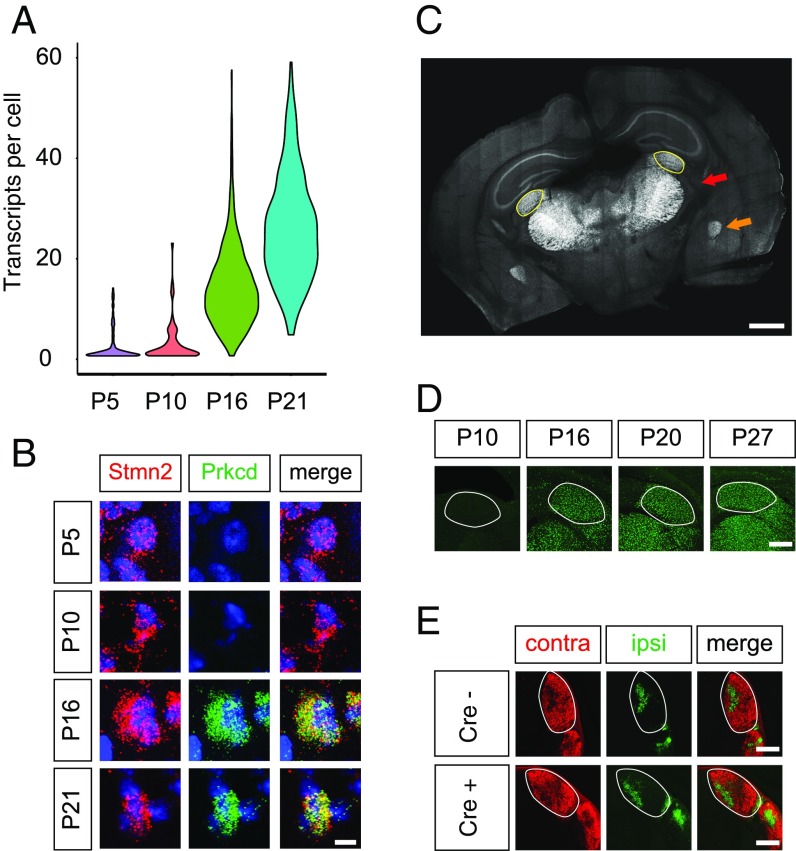
Fig. 4.
Prkcd-Cre mouse as a tool for interrogating late-stage experience-dependent synaptic refinement. (A) Violin plot displaying expression of Prkcd in excitatory neurons across development. (B) Confocal FISH images validating up-regulation of Prkcd in excitatory neurons of the LGN between P10 and P16. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (C) Coronal section of P16 mouse brain demonstrating CFP fluorescence in Cre-positive cells. Note that excitatory neurons across the thalamus are labeled with CFP. The dorsal LGN is outlined in yellow. Red arrow indicates thalamus, and orange arrow indicates amygdala. (Scale bar, 500 μm.) (D) Sun1-GFP expression in Cre-positive relay neurons of the thalamus in Prkcd-Cre/LSL-Sun1-GFP mice. The LGN is outlined. (Scale bar, 200 μm.) (E) Images of choleratoxin B conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (ipsilateral; pseudocolored green) and 555 (contralateral) in Prkcd-Cre–positive mice and Cre-negative littermates, demonstrating normal segregation of eye-specific inputs in Prkcd-Cre mice. The LGN is outlined. (Scale bars, 200 μm.)