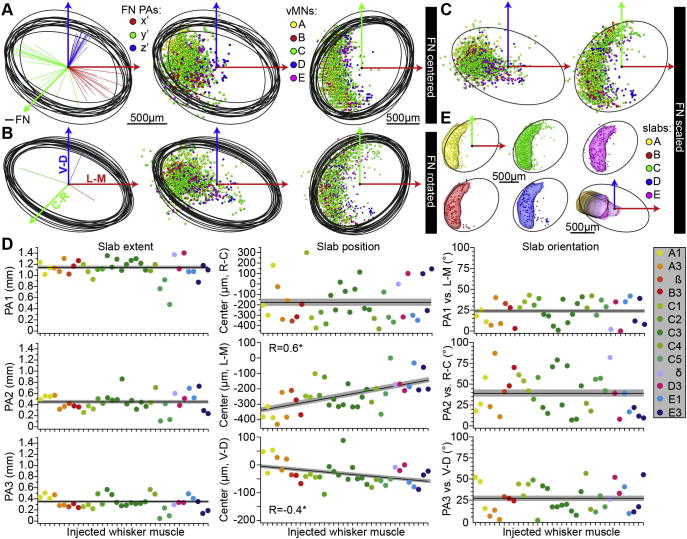
Fig. 4.
Standardized FN reference frame with vMN slabs. (A–C). The FN of all CTB-injected animals (N = 13) were approximated by an ellipsoid, whose centers of symmetry were aligned to the one of the FN reference frame (panel (A)), whose PAs were rotated to match the respective ones of the FN reference frame (panel (B)) and whose dimensions were linearly scaled to match the respective dimensions of the FN reference frame (panel (C)). In all panels, the respective distributions of retrogradely labeled somata were transformed accordingly. (D) After registration, each vMN slab was approximated by an ellipsoid (n = 36) and their respective geometrical parameters are plotted after sorting them by whisker row and then by arc (i.e. from left to right: A1–E3). The black lines and gray-shaded areas represent the mean and SEM of the respective parameter in each panel. Left: The 3D extent of the ellipsoids (i.e. length of the three PAs) did not correlate with the location of a particular whisker along the row or arc. Center: The slab ellipsoids’ center locations along the L–M and V–D axes (but not along the R–C axis) did correlate with the location of a particular whisker along the row (but not along the arc). Right: The 3D orientations of the slab ellipsoids did also not correlate with the location of a particular whisker along the row or arc. (E) Geometrical reference frame of the rat FN including an average map of whisker row-specific slabs. Slab positions represent the mean of the respective parameters shown in panel (D). Slab sizes and orientations are equal for all slabs and based on the C-row slab (see Experimental Procedures).