Figure 2. Functional role of TEFM domains.
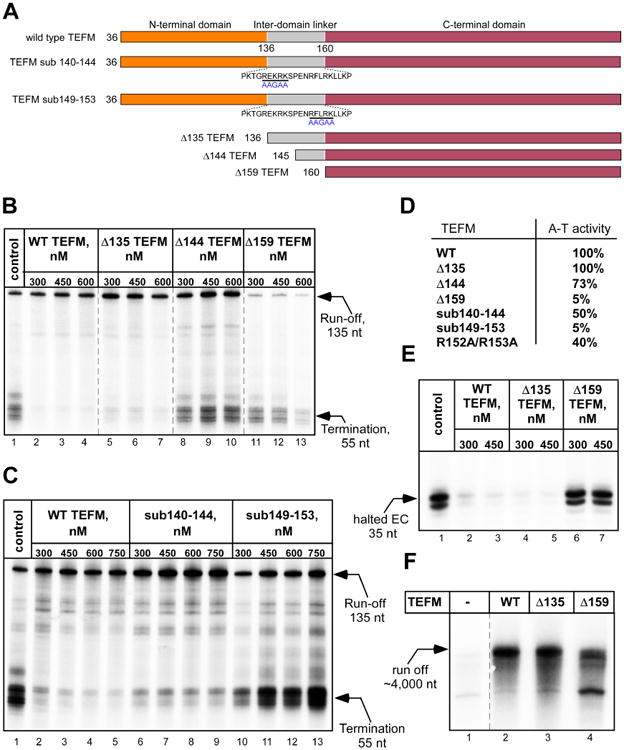
(A) Schematic representation of the TEFM NTD truncation mutants and inter-domain linker substation mutants used. Residues substituted are underlined with a black bar and the replacing residues are shown in blue beneath.
(B) TEFM CTD with the linker are required for anti-termination activity. Transcription assays were performed using a PCR template containing LSP and the CSBII region. The control reaction (lane 1) contains no TEFM. The reaction products were resolved using 20% PAGE containing 6M Urea.
(C, D) Anti-termination activity of TEFM variants having substitutions in the inter-domain linker.
(E) The NTD of TEFM is not required for the EC stability. The ECs assembled in the presence or absence of TEFM variants were halted 35 nt downstream of the transcription start site by omitting CTP. Upon incubation, the complexes were chased with CTP and the products of the reaction resolved using 20% PAGE containing 6M Urea. The region of the gel containing the 35 nt RNA is shown.
(F). Only the CTD of TEFM is required for mtRNAP processivity. Transcription was performed using a linearized plasmid template containing the LSP promoter to generate ∼4000 nt run-off product.
