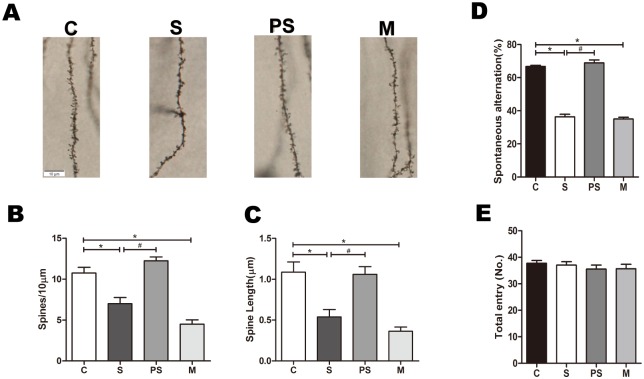
Fig 1. Sevoflurane impaired the dendritic spine morphology and memory function of 2-month-old rats.
Golgi-Cox staining was performed for the dendritic spine density and length in stratum radiatum neurons of CA1 area in 2-month-old rats (A). Sevoflurane induced significant decreases in both dendritic spine density and length. n = 8 for each group; compared with group C, *P<0.01, ANOVA. α7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 prevented changes in dendritic spine density and length. n = 8 for each group; compared with group S, #P<0.01, ANOVA. α7nAChR antagonist MLA induced significant decreases in dendritic spine density and length. n = 8 for each group; compared with group C, *P<0.01, ANOVA (B and C). In the Y-maze test (D), sevoflurane significantly decreased the percentage of spontaneous alternation in 2-month-old rats. n = 16 for each group; compared with group C, *P<0.01, ANOVA. α7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 prevented change in the percentage of spontaneous alternation. n = 16 for each group; compared with group S, #P<0.01, ANOVA. α7nAChR antagonist MLA significantly decreased the percentage of spontaneous alternation. n = 16 for each group; compared with group C, *P<0.01, ANOVA. The total arm entries in Y-maze test were not different among the groups of 2-month-old rats (E).