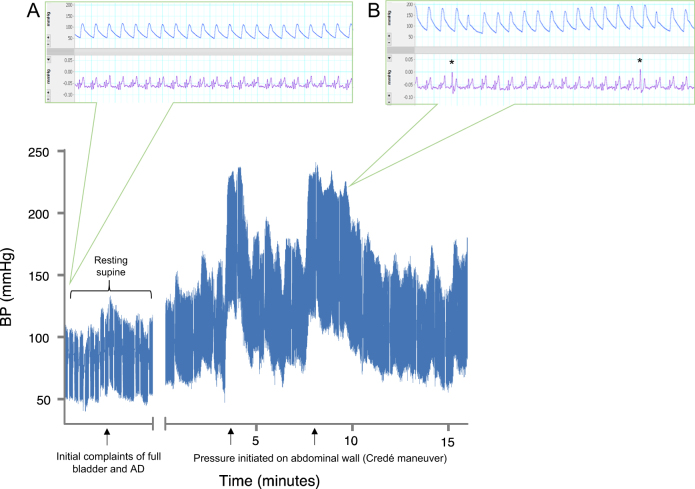
Fig. 2. Blood pressure elevation and electrocardiogram abnormalities upon bladder distension and emptying.
. Differences were observed in beat-by-beat blood pressure (BP) and electrocardiogram (ECG) between baseline condition and during bladder filling and emptying via the Credé maneuver. Baseline supine systolic BP was 100 mmHg with normal ECG trace as shown in a 25-s excerpt (a). Elevation in systolic BP occurred due to bladder distension. When systolic BP reached 130 mmHg, the patient reported a headache and flushing of the face was observed. Initiation of rhythmic pressure to the abdomen caused an immediate rise in systolic BP above 200 mmHg consistent with the episode of autonomic dysreflexia (AD). Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) occurred concurrently with bradycardia during the AD episode, as denoted by (*) and shown in a 25-s excerpt (b)