Figure 2.
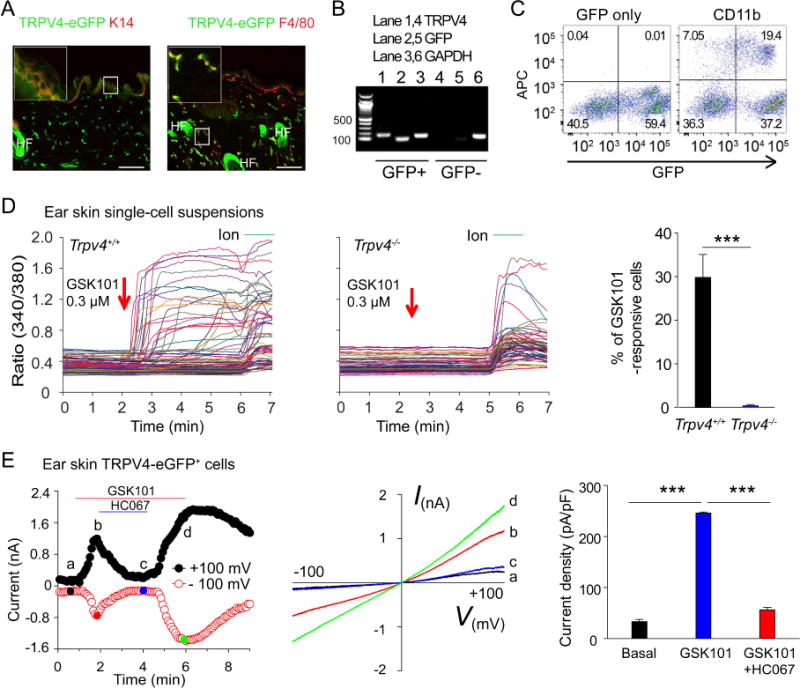
TRPV4 is functionally expressed by mouse skin-resident cells. A, Double labeling reveals the co-localization of TRPV4-eGFP with K14 (left panel) and F4/80 (right panel) in skin sections from the Trpv4eGFP mice. Bar=50 μm. HF: hair follicle. Inset shows the magnification of boxed area. B, RT-PCR shows the correlation between TRPV4 and GFP in sorted GFP+ and GFP− ear skin single-cell suspensions. C, Flow cytometry analysis illustrates that TRPV4-eGFP is expressed in CD11b-positive skin-resident cells. D, Representative traces showing the GSK101-elicited large [Ca2+]i responses in freshly dissociated ear skin single-cell suspensions from Trpv4+/+ (left) but not Trpv4−/− (middle) mice. Arrows indicate the time points of GSK101 applications. Ionomycin (Ion) was used as positive control. Summarized data from in the right showing the percentages of GSK101-responsive skin cells isolated from the Trpv4+/+ and Trpv4−/− mice. ***p<0.001, Student’s t test; n=5–8. E, Time course (left) and representative current-voltage curves (middle) elicited by voltage ramps in the absence or presence of 0.3 μM GSK101 in the TRPV4-eGFP+ myeloid cells from the ear skin single-cell suspensions. HC067 at 5 μM markedly inhibited the GSK101-activated currents. Bar charts in the right illustrate summarized data. ***p<0.001, ANOVA; n=5.
