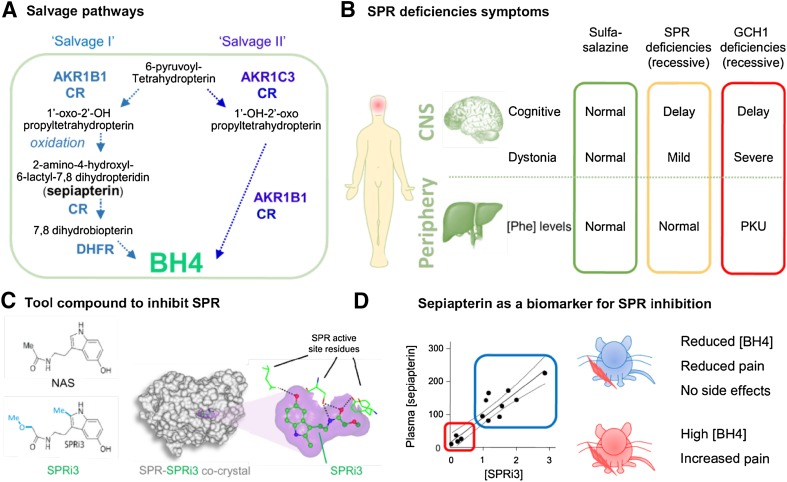
Fig. 4.
Targeting the BH4 pathway to reduce pain hypersensitivity. A Description of the salvage pathways that can produce essential cellular BH4 in the absence of SPR. Note that sepiapterin is not an endogenous SPR ligand and can only be produced when SPR is inactive. B Description of symptoms associated with recessive SPR and GCH1 deficiencies and after sulfasalazine treatment, a recently-identified SPR inhibitor. Most symptoms of SPR deficiency are central and happen during development. C A potent inhibitor was designed using a structure-based approach from N-acetyl-serotonin (NAS) to better fit the active pocket of SPR, and this was confirmed by co-crystal analysis. D Sepiapterin is a reliable biomarker for SPR inhibition that can be measured in plasma and confirms target engagement. Low levels of sepiapterin correspond to insufficient SPR inhibition, high BH4 levels, and pain hypersensitivity. High levels of sepiapterin indicate strong SPR inhibition, reduced BH4 levels, and reduced pain hypersensitivity. At these doses, no major side-effects were observed. PKU, phenylketonuria (= hyperphenylalaninemia).