Fig. 1.
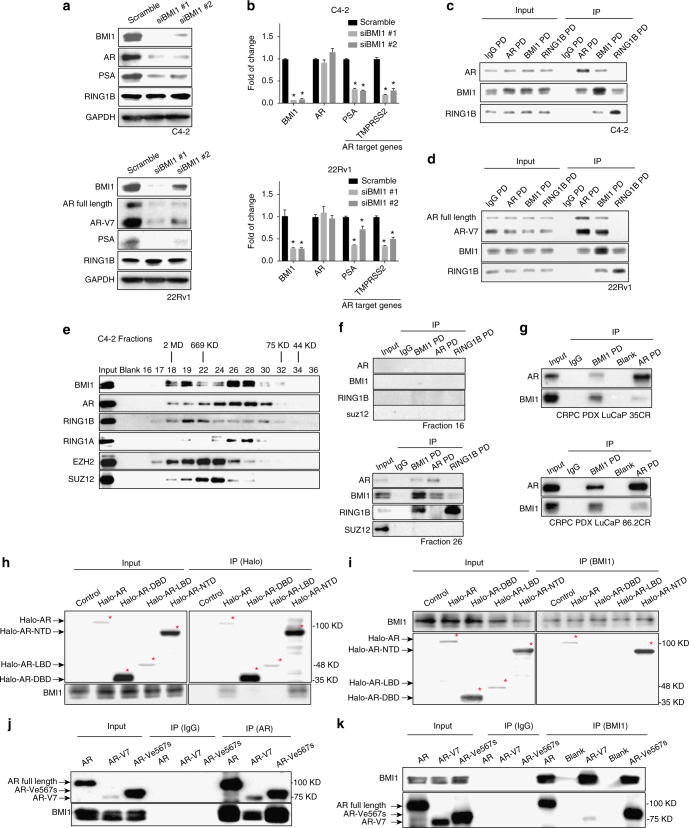
BMI1 knockdown inhibits AR signaling and BMI1 interacts with AR-NTD. a Protein levels following BMI1 depletion using two independent siRNA strands targeted at BMI1 (siBMI1 #1, siBMI1#2) in C4-2 cells (top panel) and 22Rv1 cells (bottom panel). b Transcript levels of AR and its target genes in C4-2 (top panel) and 22Rv1 cells (bottom panel) post BMI1 depletion were quantified by quantitative PCR, *P < 0.05 vs. Scramble (normalized to β-actin mRNA, mean ± SEM, n = 3). c, d Immunoprecipitations of C4-2 (c) and 22Rv1 cells (d) using anti-AR, anti-BMI1, or anti-RING1B antibody, rabbit IgG as control, followed by immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies. e Nuclear extracts from C4-2 cells were fractionated on a Sephacryl S-300 high-resolution column. The fractions were subjected to immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies. f Fractions #16 and #26 from C4-2 nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-BMI1, anti-AR, or anti-RING1B, rabbit IgG as control, followed by immunoblot analysis using indicated antibodies. g PDX tissues were lysed and subjected to pull-down assay using anti-BMI1 or anti-AR antibody, rabbit IgG as control. h 293T cells transfected with Halo-AR (full length), Halo-DBD, Halo-LBD, Halo-NTD plasmids, or empty vector were lysed and subjected to pull-down assay using halo-tag magnetic beads or i anti-BMI1 antibody followed by immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies. j 293T cells were transfected with full-length wild-type AR, AR-V7, and AR-Ve567s, respectively, followed by IPs with an anti-AR antibody or k an anti-BMI1 antibody, rabbit IgG as control. Total cell lysates served as loading control to detect input levels of BMI1, full-length AR, and AR domains. All experiments were biologically repeated at least three times. Representative images are shown