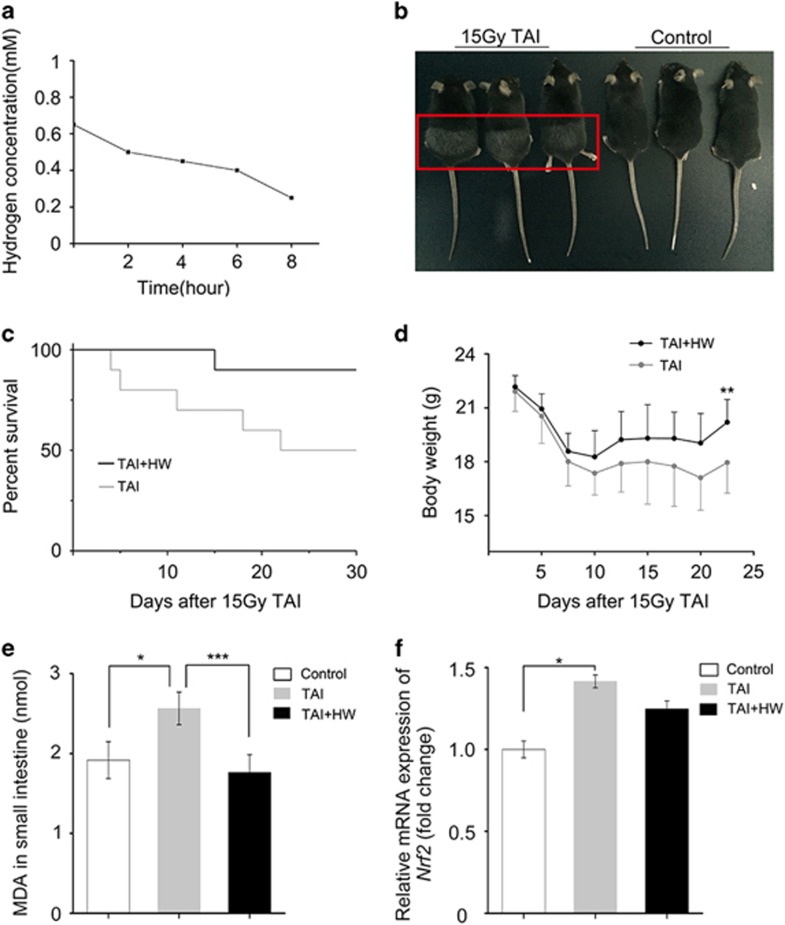
Figure 1.
Oral gavage with hydrogen-water protects mice against radiation-induced toxicity. Mice were treated with hydrogen-water 2 days before and 7 days after receiving 15 Gy TAI. (a) Direct examination of H2 concentrations over an 8-h period. (b) A mouse treated with 15 Gy TAI (left) and its littermate without irradiation (right). Note the change in fur color in the irradiated lower body. (c) Kaplan–Meier analysis of hydrogen-water- and normal water-treated mice after 15 Gy TAI. P<0.05 by log-rank test between TAI-exposed mice with or without hydrogen-water treatment, n=12. (d) Body weight was compared between hydrogen-water- and saline-treated mice after 15 Gy TAI. n=12; **P<0.01; Student’s t-test. (e) The level of MDA in the small intestine was compared among the healthy control, 12 Gy TAI and hydrogen-water groups. n=12; *P<0.05; **P<0.01;***P<0.005; Student’s t-test. (f) The expression levels of Nrf2 were assessed in small intestine tissue from the healthy control, 12 Gy TAI and hydrogen-water groups. n=12; *P<0.05; Student’s t-test.