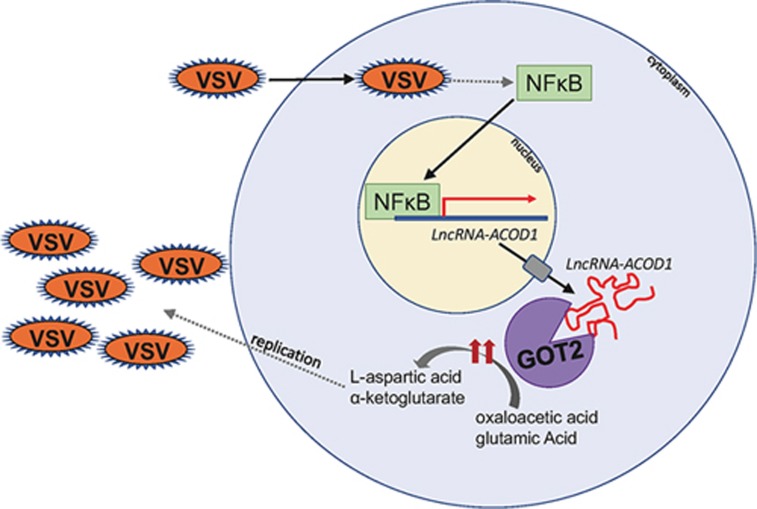
Figure 1.
Vesicular stomatitis virus infects a macrophage, leading to activation and nuclear translocation of NFκB. This allows for transcription of lncRNA-ACOD1, which is then exported into the cytoplasm. LncRNA-ACOD1 directly binds GOT2, boosting its enzymatic activity. GOT2 converts oxaloacetic acid and glutamic acid into α-ketoglutarate and L-aspartic acid; these metabolic products promote viral replication.