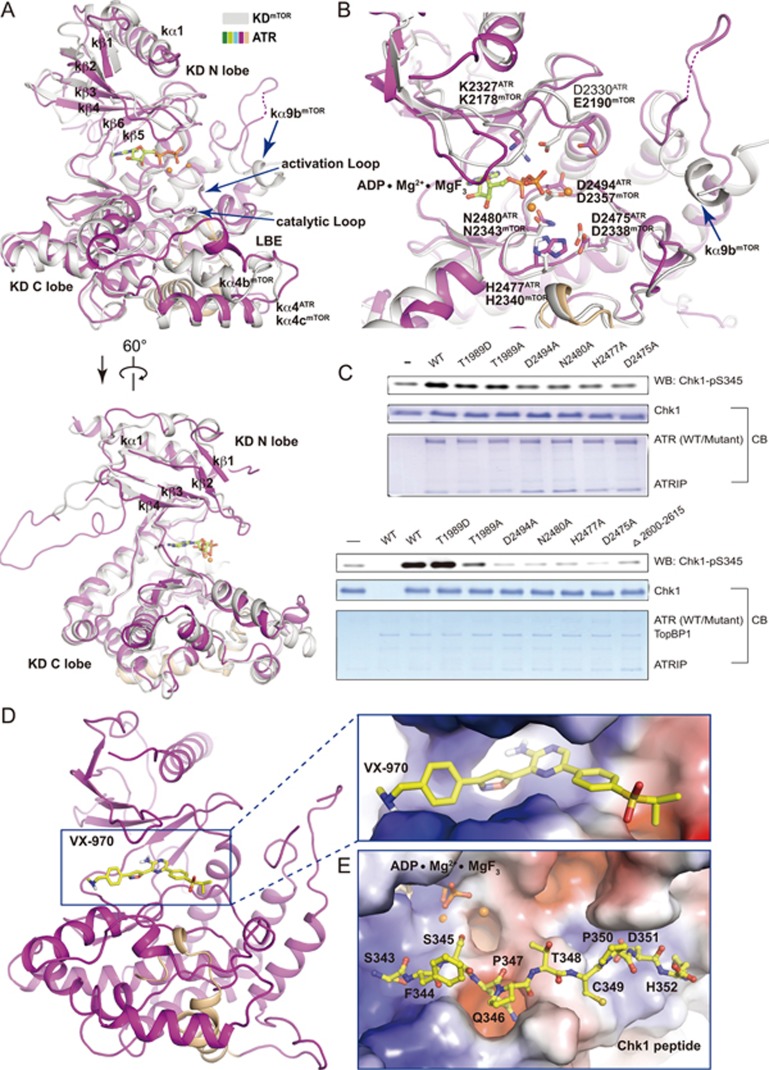
Figure 3.
The kinase domain of ATR. (A, B) Two different views of superimposed kinase domains of mTOR and ATR. The same color scheme for ATR is used as in Figure 1A and mTOR is colored in grey. The FRB domain of mTOR is omitted for simplicity. In the mTOR structure, ADP is shown in stick representation and two Mg2+ cations are shown as orange balls. Residues involved in catalysis for mTOR and ATR are shown in stick representation and indicated. Invisible regions are connected by dashed lines. (C) In vitro kinase activity assay using purified ATR (wild-type or mutant)-ATRIP. Purified human Chk1 (3.5 μM) serves as substrate. 250 nM (upper panel) or 5 nM (lower panel) ATR-ATRIP was used in the presence or the absence of TopBP1 (25 nM), respectively. (D, E) Docking of VX-970 (D) and a Chk1 peptide (residues 343-352) (E) into the KD structure. Close-up views with electrostatic potential surface of ATR catalytic cavity (D) and substrate-binding groove (E) are shown, respectively. VX-970 and the Chk1 peptide are shown in stick representations. The carbon atoms are colored in yellow, oxygen in red, and nitrogen in blue.