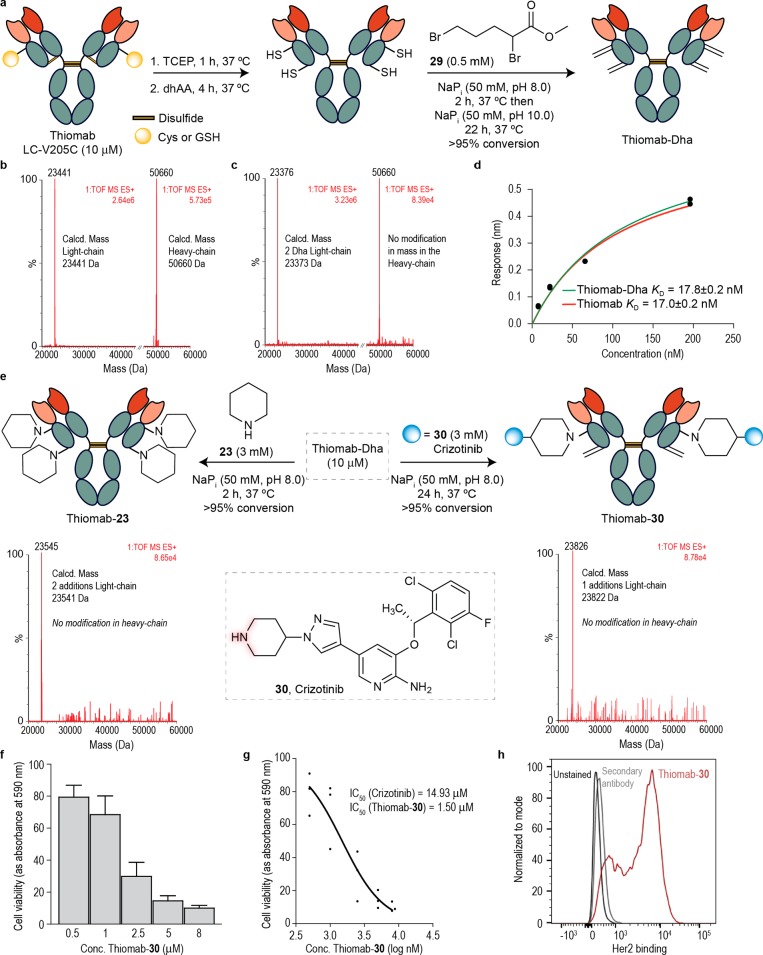
Figure 6.
Construction of a stable and chemically defined ADC through direct, aza-Michael conjugation of crizotinib to Dha-tagged Thiomab and its biological evaluation. (a) Reaction scheme for the conversion of Thiomab LC-V205C to Thiomab-Dha using a bis-alkylation/elimination procedure. (b) ESI–MS spectra of the light- and heavy-chains of Thiomab LC-V205C after reduction and reoxidation protocol. (c) ESI–MS spectra of the light- and heavy-chains of the reaction of Thiomab LC-V205C with methyl 2,5-dibromopentanoate 29 shows the formation of two Dha residues per light-chain. (d) KD constants derived from BLI experiments for Thiomab and Thiomab-Dha. For the BLI curves and fitting curves obtained for Thiomab and Thiomab-30 with Her2 receptor see the SI. (e) Reaction scheme for the reaction of Thiomab-Dha with either piperidine 23 or crizotinib 30. ESI-MS spectra of the light-chain shows the addition of two piperidine molecules and the addition of one crizotinib 30, respectively. (f) SKBR3 cells viability after treatment with Thiomab-30 for 24 h. See SI for data with crizotinib and naked Thiomab (control). Results are shown as percentage of control (medium + vehicle – PBS) and correspond to 3 biological replicates (mean ± s.d.). (g) IC50 of Thiomab-30 in SKBR3 cells. (h) Thiomab-30 binding affinity to SKBR3 cells measured by flow cytometry.