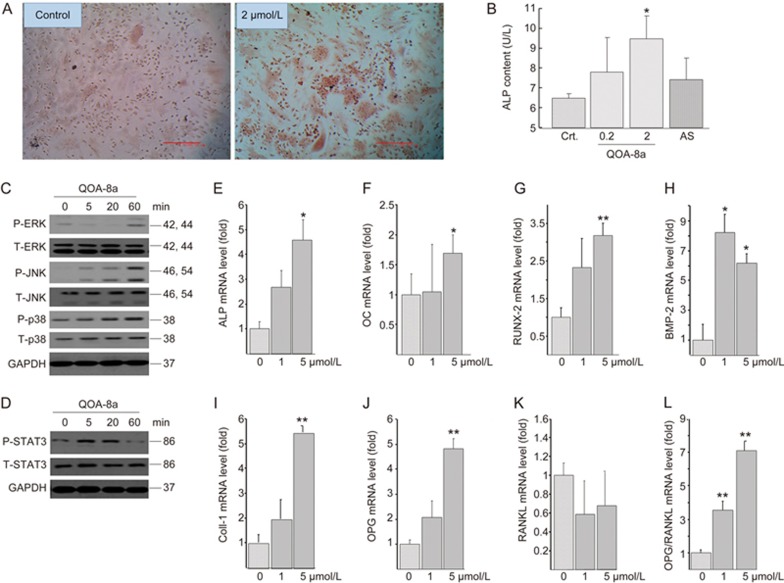
Figure 7.
Osteogenic effects and signaling involved in stimulating osteoblast differentiation by QOA-8a. (A) The Alizarin Red staining on primary BMMSCs incubated with vehicle (DMSO) or with QOA-8a (2 μmol/L) in the presence of β-glycerol phosphate (10 mmol/L), ascorbate-2-phosphate (50 μg/mL) and dexamethasone (10−7 mol/L) for 7 d. (B) Effects of QOA-8a on the ALP activity in osteoblast differentiated from primary BMMSCs for 7 d. ALP in aliquots of supernatants from vehicle (DMSO), QOA-8a (0.2, 2 μmol/L) or AS (2 μmol/L) was measured by an ALP activity kit. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05. For signaling experiment, mouse calvarial osteoblastic cell line MC3T3-E1 was treated with 5 μmol/L QOA-8a in a time-course experiment, and Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, JNK, p38 activating phosphorylation (C), and STAT3 activating phosphorylation (D). (E–K) Osteoblast differentiation marker expression assessed by real-time qPCR in MC3T3-E1 cells treated with different doses of QOA-8a for 12 h, normalized versus actin. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (L) The ratio of OPG and RANKL mRNA expression.