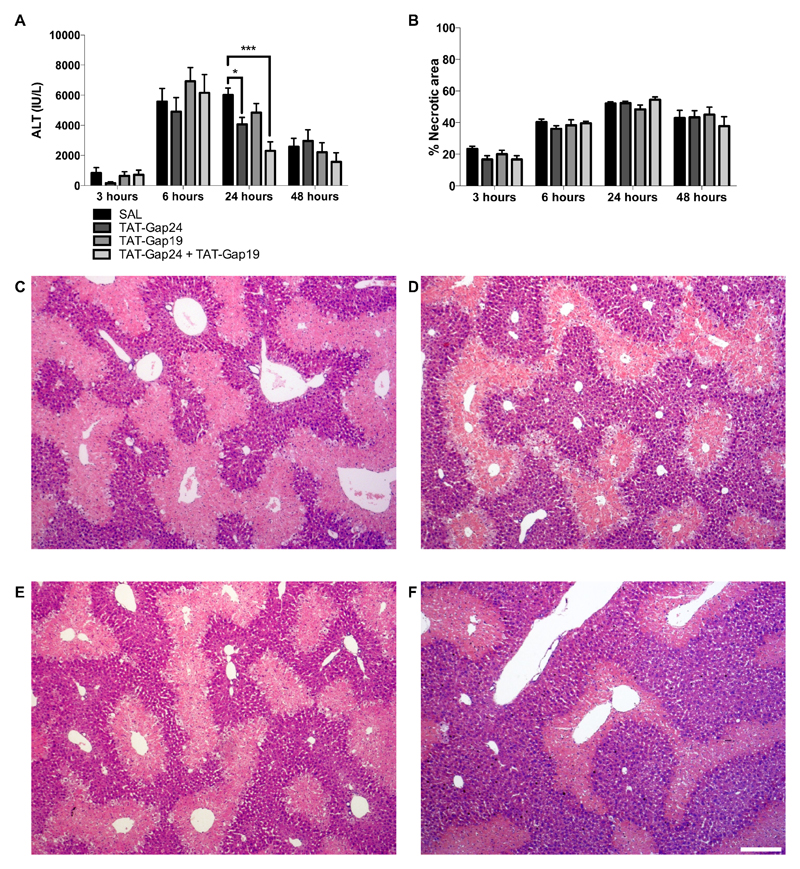
Figure 3. Connexin hemichannel inhibition diminishes liver cell damage in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity.
Mice (n = 5-20 per group and per time point) were injected 300 mg/kg APAP followed by administration of 10 mg/kg TAT-Gap24, 10 mg/kg TAT-Gap19, a combination of both or saline (SAL) 1.5 hour later. Sampling was performed 3, 6, 24 and 48 hours after APAP overdosing. (A) Serum levels of ALT were measured with an automated spectrophotometer and expressed as IU/L. (B) Liver sections were examined microscopically with quantification of the necrotic areas around the central veins. Data are expressed as means ± SEM, with *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 compared to APAP followed by SAL administration. Microscopic pictures of the liver tissue 24 hours after APAP administration followed by (C) SAL, (D) 10 mg/kg TAT-Gap24, (E) 10 mg/kg TAT-Gap19 or (F) a combination of 10 mg/kg TAT-Gap24 and TAT-Gap19. The white scale bar represents 200 µm.