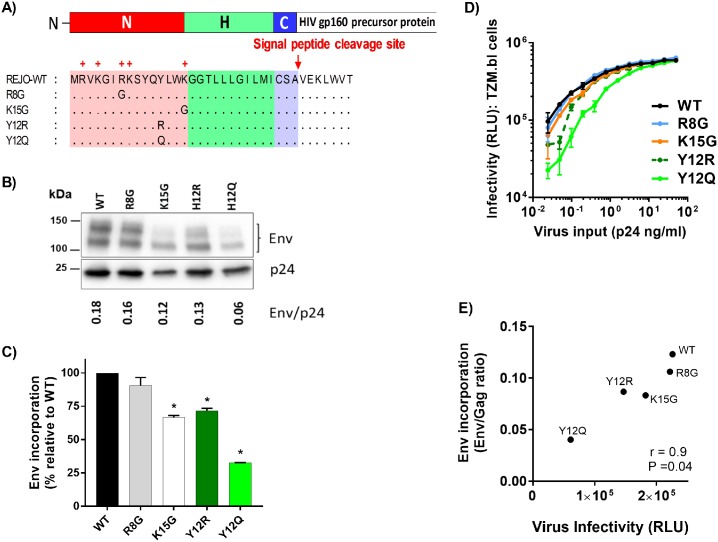
Fig 9. Effects of SP mutations on JRFL Env expression, virus infectivity and reactivity to different MAbs.
(A) Schematic representation of JRFL WT and four different SP mutations evaluated in this study. (B) Measurement of Env incorporation by Western blot. JRFL WT and mutant viruses were produced in transfected 293T cells, lysed, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (4–20%) and Western blot. An anti-gp120 MAb cocktail (V3: 391/95-D, 694/98-D, 2219, 2558; C2: 847-D, 1006-30D; C5: 450-D, 670-D) and a p24 Gag MAb (91–5) were used to detect the relative levels of Env and Gag associated with virions. The ratios of Env/Gag were calculated. (C) The levels of Env incorporation into JRFL mutant virions relative to that of WT were calculated based on their Env/Gag ratios (WT value was set to 100%). *, p< 0.01 (ANOVA). (D) Infectivity of JRFL WT vs. mutant viruses in CD4+ TZM.bl cells exposed to titrated viruses with equivalent p24 contents. (E) Correlation of virus infectivity in CD4+ TZM.bl cells with Env incorporation into the virions by Spearman’s rank test. Virus infectivity was based on RLU produced upon infection with a fix amount of virus input (0.9 ng p24/ml).