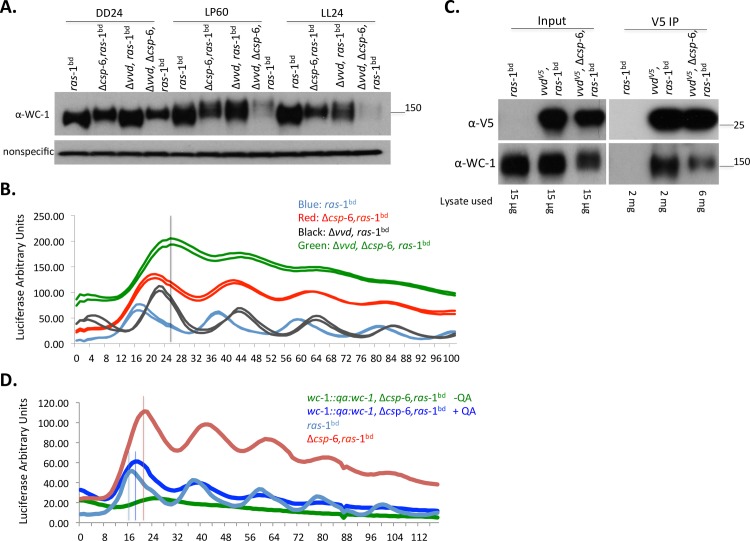
Fig 4. Reduced interaction between WC-1 and VVD in the Δcsp-6 mutant affects WC-1 phosphorylation and the phase of frq expression.
A: Western blot analyses showing WC-1 levels in ras-1bd; Δcsp-6 ras-1bd, Δvvd, ras-1bd and Δcsp-6, Δvvd, ras-1bd under indicated conditions. B: Representative luciferase traces of frq c-box-luc showing a further phase delay in the Δcsp-6, Δvvd double mutant as compared to either single mutant. C: VVD-WC-1 interaction at LP60min in both vvdV5 and vvdV5,Δcsp-6 in the ras-1bd background; ras-1bd was used as negative control. VVD-V5 was immunoprecipitated using anti-V5 agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using WC-1 antibody. Because reduced WC-1 was detected in the Δcsp-6 mutant, we used three times more extract for the IP of vvdV5, Δcsp-6 (6mg) than those of wild type (2mg) background, based on the quantification by Western blot (S4A Fig) to make sure similar amounts of WC-1 were available for IP. D: Representative luciferase activity assays of frq-luc in strain wc-1::qa:wc-1, Δcsp-6 in the presence or absence of 0.01M QA, showing that increased WC-1 levels can partially rescue the phase delay phenotype of Δcsp-6.