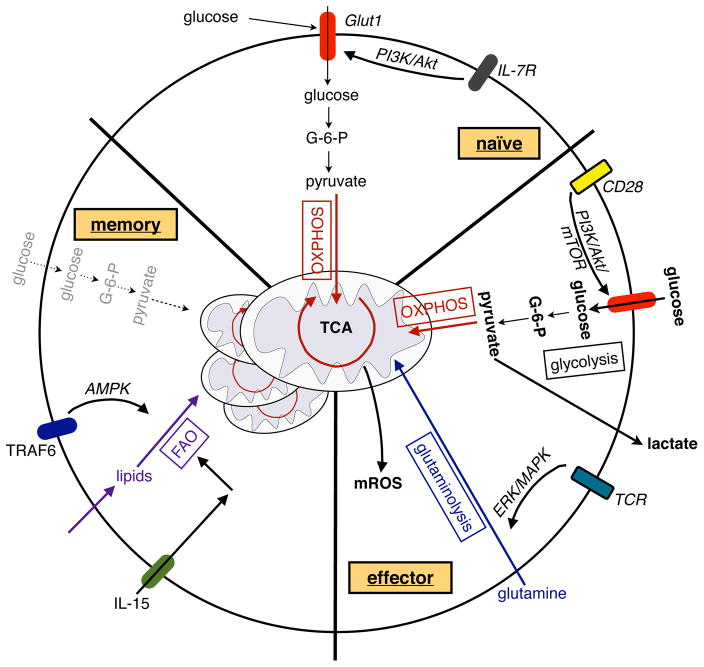
Figure 4. Metabolism of naïve, activated and memory T cells.
Signaling via the IL-7 receptor (IL-7R) maintains Glut1 expression, glucose uptake, and mitochondrial OXPHOS in naïve CD4+ T cells. Upon activation, signaling via CD28 activates the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to induce glycolysis in activated T cells, whereas TCR-driven ERK/MAPK signaling initiates glutaminolysis to support T cell proliferation. In addition, glycolysis promotes the translation of cytokines in activated T cells. In metabolically restrictive environments, OXPHOS can promote the proliferation of activated T cells, whereas mROS can enhance antigen-specific T cell activation. In contrast to the activation of T cells, memory formation of CD8+ T cells is dependent on TRAF6 and IL-15 driven FAO and mitochondrial biogenesis; the former is, in part, supported by activation of the cellular energy sensor AMPK.