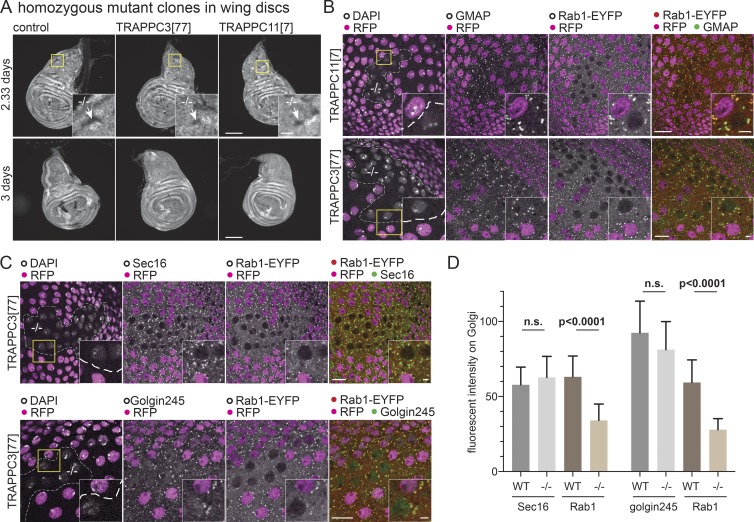
Figure 6.
TRAPPIII is required for cell growth and Rab1 localization. (A) Widefield micrographs of wing imaginal discs in which mitotic clones had been induced using the Flp-FRT system 2.33 or 3 d before fixation. This method generates homozygous clones of cells in a heterozygous background. The control clones or clones mutant for TRAPPC3[77] or TRAPPC11[7] are marked by the absence of RFP-tagged histone that is expressed from the chromosome that carries the mutation (arrows in inset zoom). Clones lacking TRAPPC3 or TRAPPC11 are only detectable at the earlier time point. Bars: (main images) 100 µm; (insets) 20 µm. (B and C) Confocal micrographs of YFP-Rab1 in clones of cells mutant for TRAPPC11[7] or TRAPPC3[77] in the peripodial cells of the wing imaginal discs costained for YFP and the Golgi markers GMAP or Golgin245 or the ER exit site marker Sec16. Mutant clones are marked by loss of RFP-tagged histone, with the nuclei stained with DAPI. Loss of TRAPPC11 or TRAPPC3 reduces YFP-Rab1 on the Golgi without affecting the other markers. Bars: (main images) 10 µm; (insets) 2 µm. Images are representative of at least two independent experiments, with at least three micrographs obtained from each. (D) Comparison of the levels on the Golgi of YFP-Rab1 and of Golgi/ER exit site markers in the homozygous mutant clones for TRAPPC3−/− versus the surrounding WT tissue. Fluorescent intensities were extracted from micrographs such as those shown in C, and in each case, n = 20 Golgi from two wing discs. Mean values are shown. Error bars show SD. The level of YFP-Rab1 showed a statistically significant reduction in the mutant clones, whereas the other markers were not significantly affected (two-tailed nonparametric Mann-Whitney test).