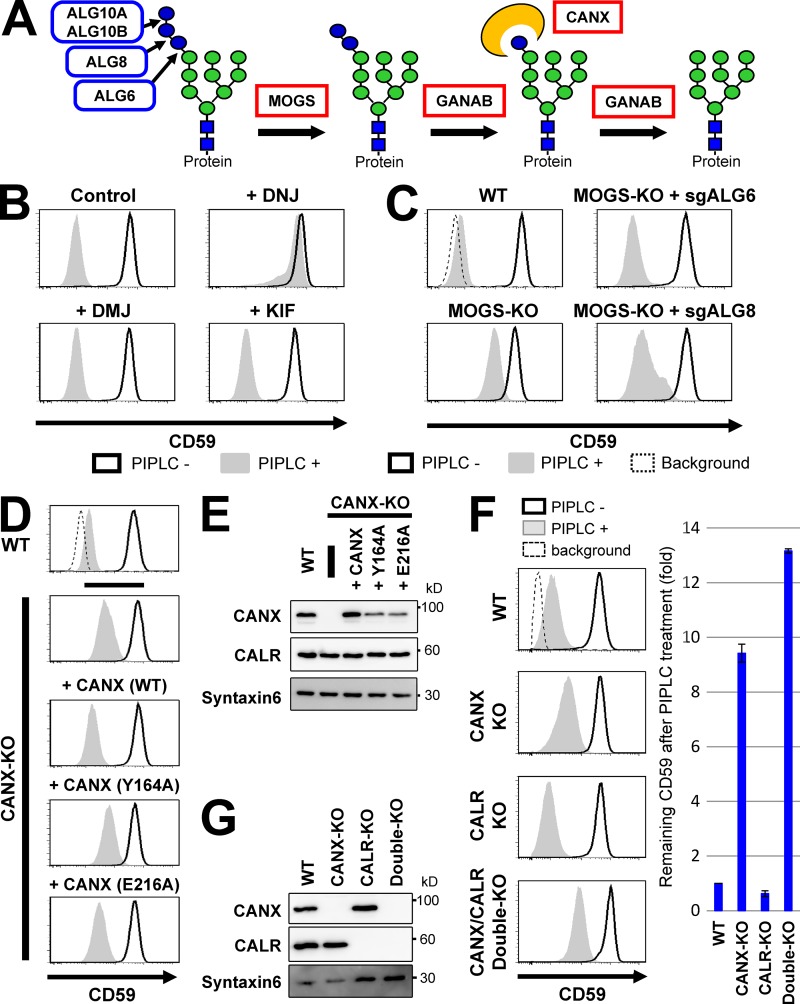
Figure 4.
Glucose trimming from N-glycans and calnexin affected GPI-inositol deacylation. (A) Schematic of glucose trimming after protein N-glycosylation. ALG6, ALG8, and ALG10 are enzymes that add three glucoses (blue circles) one by one to the lipid-linked oligosaccharide Man9GlcNAc2 structure. MOGS and GANAB are α-glucosidase I and α-glucosidase II enzymes, removing the first and the other two glucose from N-glycans, respectively. CANX is calnexin, recognizing and binding to the monoglucosylated N-glycan structure. Green circles, mannose; blue squares, GlcNAc. (B) HEK293FF6 cells were treated with DNJ, an α-glucosidase inhibitor, or DMJ or KIF, α1,2-mannosidase inhibitors, for 11 d. Flow cytometry was used to analyze surface CD59 in cells with or without PIPLC treatment as described in Fig. 2 A. (C) MOGS-KO cells were transfected with plasmids expressing single guide (sg) ALG6 or sgALG8 RNAs to knock out those genes. Plasmid-positive cells were sorted and cultured for >10 d after transfection. Flow cytometry analysis of the surface CD59 in cells with or without PIPLC treatment was performed as described in Fig. 2 A. (D) Resistance of GPI-APs against PIPLC in CANX-KO cells was rescued by expression of WT but not lectin activity–deficient calnexin. WT cells and CANX-KO cells stably expressing WT CANX or mutant CANXs (Y164A or E216A) were treated with or without PIPLC. After treatment, cells were stained with anti-CD59 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry as described in Fig. 2 A. (E) Lysates of cells in D were analyzed by Western blotting. CANX and CALR were detected. Syntaxin 6 was used as the loading control. (F and G) WT, CANX-KO, CALR-KO, and CANX/CALR double-KO cells were treated with or without PIPLC. Flow cytometry analysis of surface CD59 was performed (F) as described in Fig. 2 A. CD59 levels remaining after PIPLC treatment are plotted. The remaining CD59 value in WT cells was set as 1. Relative values were calculated and are shown as means ± SD from three independent experiments. Lysates prepared from cells were analyzed by Western blotting (G).