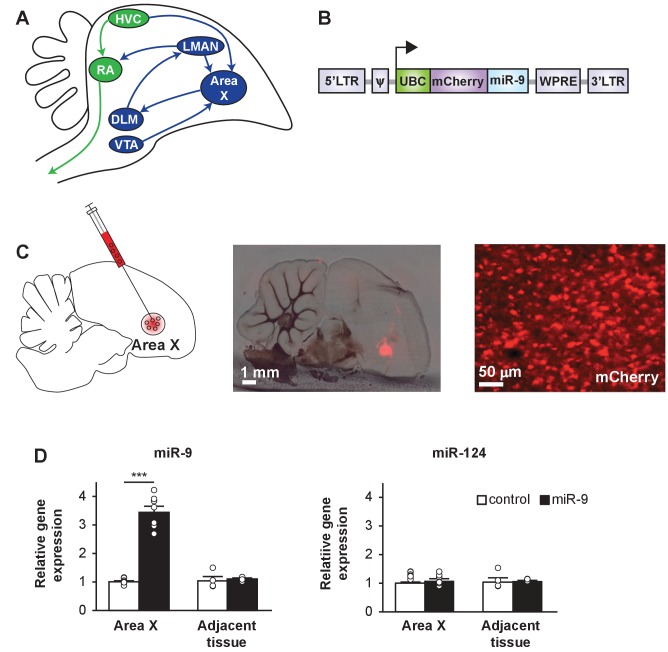
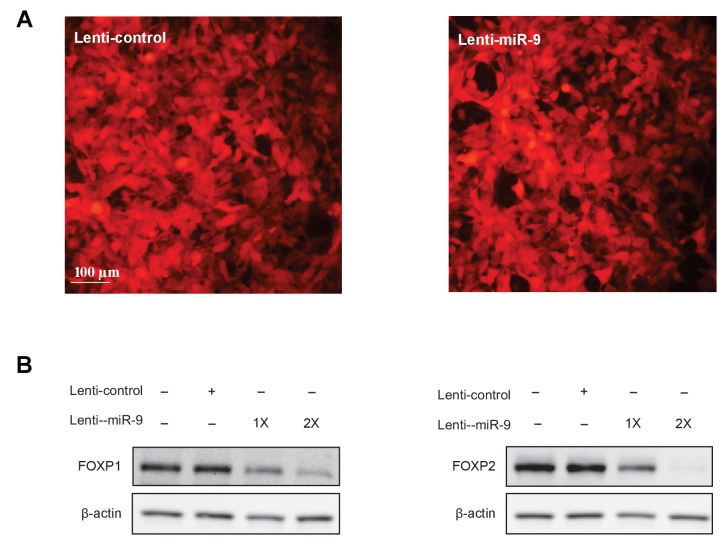
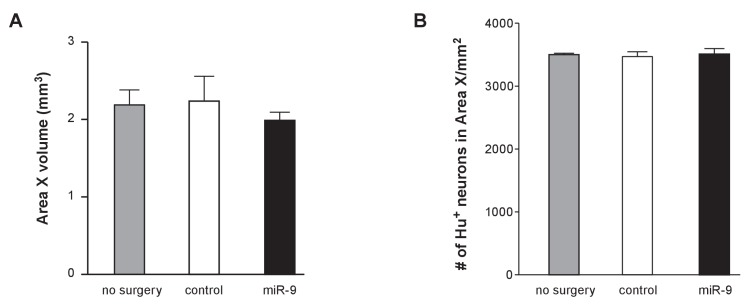
Figure 1. A lentiviral approach to manipulate miR-9 expression in Area X of the zebra finch brain.
(A) Schematic drawing of the song control circuit in the zebra finch brain. The motor pathway (green), which connects HVC (used as a proper name) to RA (robust nucleus of the arcopallium) and eventually the vocal organ, controls song production. The anterior forebrain pathway (blue), which connects HVC to the basal ganglia nucleus Area X, DLM (medial nucleus of the dorsolateral thalamus), LMAN (lateral magnocellular nucleus), and then back to RA, is required for song learning. Area X also receives dopaminergic inputs from the VTA (ventral tegmental area). (B) The lentiviral vector used in this study expresses an mCherry fluorescent marker and miR-9 driven by the human ubiquitin promoter. (C) (Left) A diagram showing viral injection into Area X. (Middle and right) Sagittal sections of the zebra finch brain showing mCherry fluorescent signal in juvenile Area X four weeks after lentivirus injection. (D) The expression of miR-9 and miR-124 in Area X 4 weeks after injection with the lenti-miR-9 virus. p < 0.0001, t(12) = 11.21 for miR-9; p = 0.2879, t(12) = 1.112 for miR-124, unpaired t-test. n = 7 for Area X; n = 4 for adjacent tissue. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.