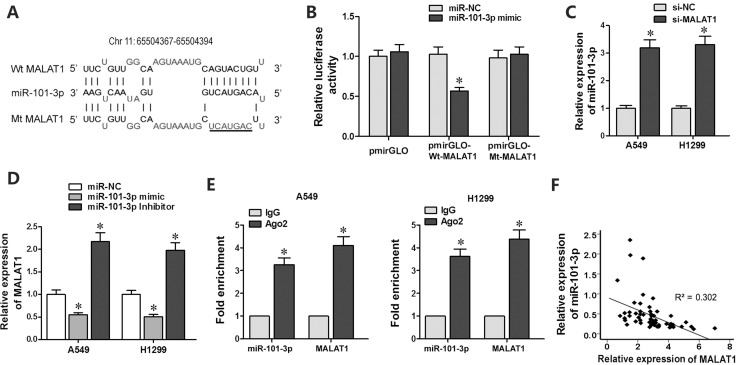
Figure 3. MiR-101-3p is a direct target of MALAT1.
(A) Predicted miR-101-3p binding site in MALAT1 sequence based on DIANA-LncBase analysis. (B) Relative luciferase activity is decreased in cells transfected with Wt-MALAT1 (wild type miR-101-3p binding site) and miR-101-3p mimics than in cells transfected with Mt-MALAT1 (mutant miR-101-3p binding site) and miR-101-3p mimics. This demonstrates that miR-101-3p directly binds to MALAT1. (C) QRT-PCR analysis of miR-101-3p levels in siMALAT1 and siNC-transfected A549 and H1299 cells at 48 h post-transfection. U6 was used as internal control. (D) QRT-PCR analysis of MALAT1 levels in A549 and H1299 cells transfected with miR-101-3p mimics, miR-101-3p inhibitor or negative control miRNA sequence at 48h post-transfection. (E) QRT-PCR analysis of miR-101-3p and MALAT1 levels isolated from Ago2 and IgG immunoprecipitates derived from A549 and H1299 cells. (F) Pearson’s analysis shows correlation between MALAT1 and miR-101-3p levels in tissue samples from lung cancer patients sensitive or resistant to cisplatin (n = 28/group; Pearson’s coefficient [R] = - 0.549).