Figure 5.
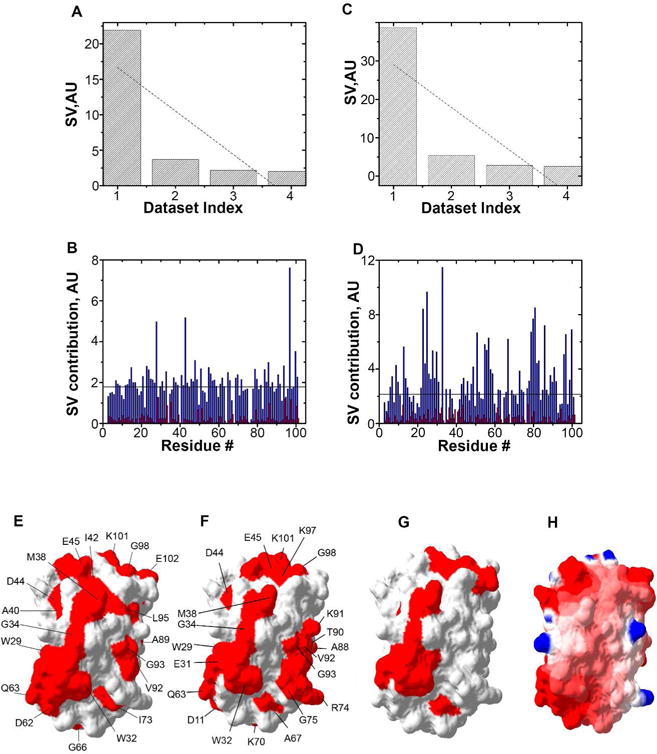
Antibiotic binding to ribosomes affects residues that match the Trx quinary interaction surface. A. Distribution of singular values, SV, of each dataset index (binding mode) for Trx residues in the presence of tetracycline. B. The contribution of each amino acid in response to adding tetracycline is shown for the first (blue) and second (red) binding modes. C. Distribution of SV of each dataset index (binding mode) for Trx residues in the presence of streptomycin. D. The contribution of each amino in response to adding streptomycin is shown for the first (blue) and second (red) binding modes. E. Residues involved in quinary interactions (red) due to the presence of tetracycline are mapped onto the molecular surface of Trx (PDB entry 1X0B). F. Residues involved in quinary interactions (red) due to the presence of streptomycin. G. Quinary interaction surface (red) of Trx in the absence of antibiotics. H. Electrostatic surface map of Trx showing regions of positive, 4 kT/e, (blue) and negative, −4 kT/e (red) potential, where k is the Boltzmann constant, T is the temperature and e is the electron charge. In A and C, linear fits of SVs are shown by dotted lines. In B and D, the horizontal line represents the threshold used to highlight the amino acids with the strongest effect on quinary structure. The threshold value was set at one and a half times the largest contribution from the second binding mode, which represents the average noise of the NMR spectra.
