Fig. 1.
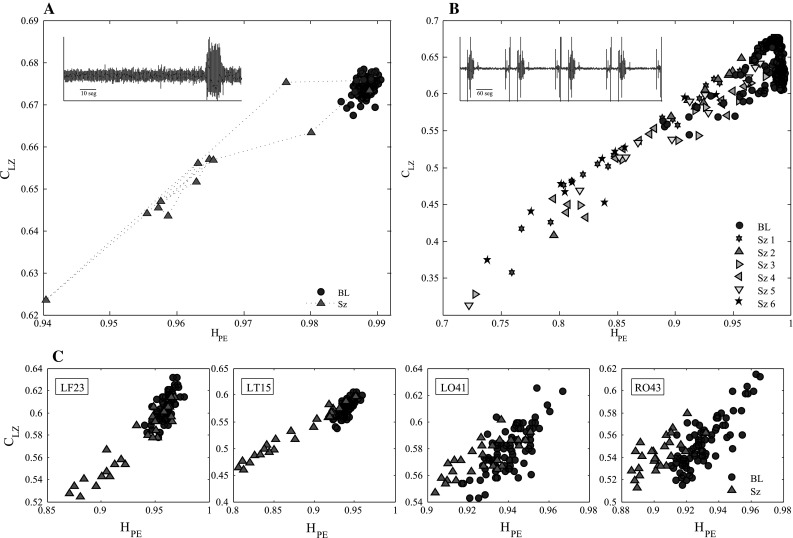
Represents the permutation Lempel Ziv complexity (PLZC) versus permutation entropy () (with parameter and ) time tracking values for MEG signal in epileptic patients during conscious, baseline (BL) and unconscious, seizure (Sz) states. a Subject 1, patient with primary generalized epilepsy; the MEG signal for one channel is plotted in the inset (the high amplitude change represents the absence seizure). We observe that before the seizure the entropy and complexity values remain very high, decreasing during the seizure and returning to the original values after the seizure. b Subject 2, patient with symptomatic generalized epilepsy, who had 7 generalized tonic seizures during the recording period, shown in the inset. When the patient is in the baseline inter-ictal (between seizure) state, entropy and complexity values are higher, decreasing during each ictal (seizure) state. c Subject 3, patient with frontal lobe epilepsy; 4 channels were analyzed separately, left frontal (LF23), left temporal (LT5), left occipital (LO41), right occipital (RO43). For the two recording areas most affected by the focal onset secondarily generalized tonic seizure (LF23 and LT5) entropy and complexity change in the ictal state, but for the areas which are not affected (LO41 and RO43), the and values are the same as in the baseline state. The same results were obtained for the parameters and
