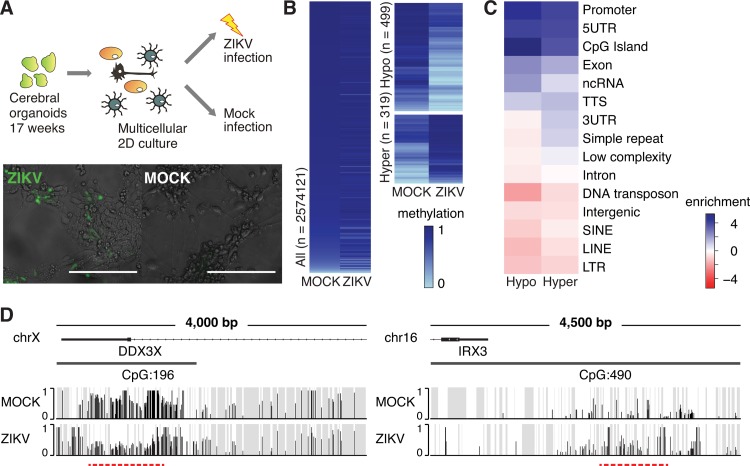
FIG 1 .
ZIKV infection induces global DNA methylation changes in multicellular human cerebral organoids. (A) (Top) Schematic of the samples used for whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS). (Bottom) ZIKV-positive cells (anti-flavivirus group E antigen, green) upon ZIKV infection (strain MR766) of cerebral organoid-derived 2D cultures. Bars, 100 µm. (B) Heat maps show methylation levels of all defined 1-kb tiles (left) and DMRs with an average methylation difference greater than 0.2 (right). (C) Enrichment [log2(hypergeometric P value)] of genomic features of differentially methylated 1-kb tiles (q value of <0.05 and methylation difference greater than 0.2). UTR, untranslated region; ncRNA, noncoding RNA; TTS, transcription termination site; SINE, short interspersed nuclear element; LINE, long interspersed nuclear element; LTR, long terminal repeat. (D) Examples of a hypomethylated (DDX3X) and hypermethylated (IRX3) gene locus. Gray, areas with nonsignificant sequencing signal; red dashed line, differentially methylated region.