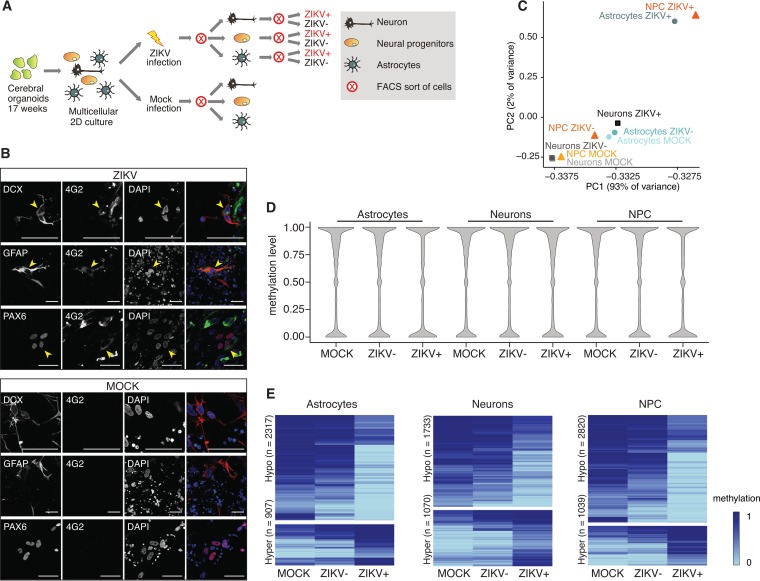
FIG 2 .
ZIKV infection induces DNA methylation changes in human cerebral organoid-derived astrocytes, neurons, and neural progenitor cells. (A) Schematic of the samples used for reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS). (B) Immunofluorescence staining of ZIKV- and mock-infected multicellular 2D cerebral organoid cultures to detect ZIKV (strain MR766) infection (4G2, anti-flavivirus group E antigen, green) in neurons (DCX, red), astrocytes (GFAP, red), and neural progenitor cells (PAX6, red). Bar, 100 µm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (C) Principal-component analysis based on the mean methylation levels of 100-bp tiles. (D) Distribution of methylation levels in samples with or without ZIKV (strain MR766) infection, as indicated. (E) Heat maps of differentially methylated 100-bp tiles in each cell type (q value of <0.05 and methylation difference greater than 0.2). NPC, neural progenitor cells.