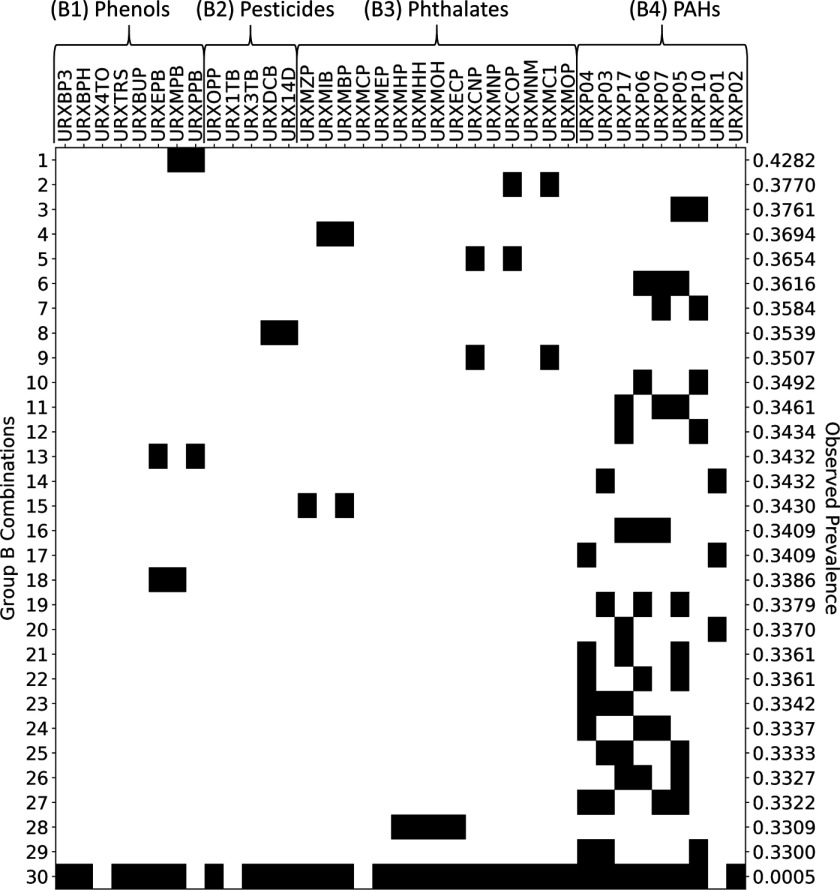
Figure 6.
Presence–absence map (black indicates present) illustrating 29 maximal prevalent combinations of Group B chemicals (rows 1 through 29) and one supercombination consisting of 32 of the 37 chemicals in Group B (row 30). The maximal prevalent combinations were identified using frequent item set mining (FIM) with discretization thresholds set at the 50th percentiles and a minimum prevalence level of 33%. The supercombination occurred in 2 Subsample B subjects, representing a total of 137,261 (or 0.05%) of 272,911,633 represented U.S. residents. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) codes along the top of the figure indicate Group B chemicals, and these are organized into subgroups B1, B2, B3, and B4. The observed prevalence number at the right of each row indicates the proportion of U.S. residents in which the given combination was observed to occur.