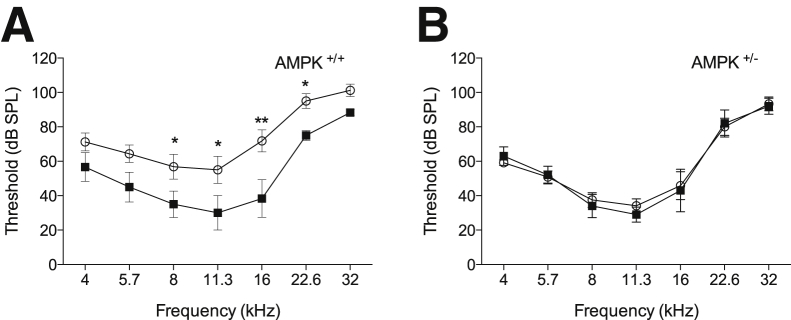
Figure 4.
Reduced AMP kinase (AMPK) α1 signaling rescues hearing loss in a transgenic mouse strain that robustly overexpresses the mitochondrial 12S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase TFB1M (Tg-mtTFB1). Auditory brainstem response thresholds of littermates of the indicated genotypes were tested at 9 to 12 months of age. A two-way analysis of variance demonstrates that the overall effect for genotype was statistically significant [F(3,126) = 17, P < 0.001]. A: All animals are AMPK+/+ (wild-type for AMPKα1) and either wild-type (non-transgenic, closed squares) or transgenic for mtTFB1 (Tg-mtTFB1, open circles). B: All animals are AMPK+/− (heterozygous for AMPKα1) and either wild-type (non-transgenic) or transgenic for mtTFB1 (Tg-mtTFB1). Results of post hoc Fisher's least significant difference tests comparing the genotypes at individual frequencies. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. db SPL, decibels sound pressure level.