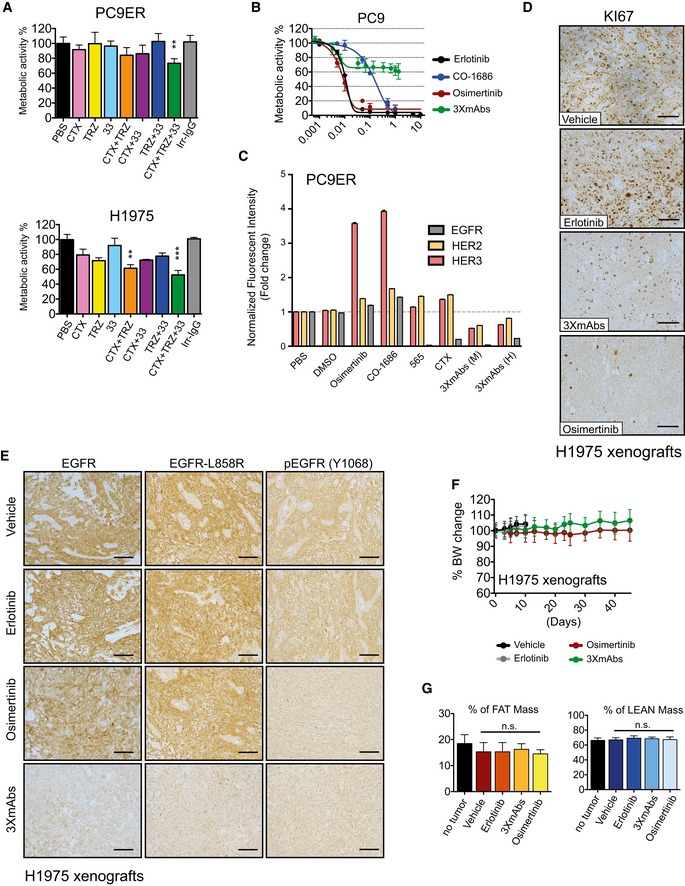
PC9ER (upper panel) and H1975 cells (lower panel) were grown in RPMI‐1640 (2% serum) and exposed for 4 days to the indicated antibodies (20 μg/ml) against EGFR (cetuximab; CTX), HER2 (trastuzumab; TRZ), or HER3 (mAb33). Whenever antibody mixtures were applied, the total antibody concentration remained constant. Cell survival was assessed using the MTT colorimetric assay. Data are means ± SD. **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; n = 3; one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's test.
PC9 cells were cultured for 4 days with increasing concentrations of either TKIs (erlotinib, osimertinib, or CO‐1686) or the triple antibody combination (CTX, TRZ, and mAb33). Metabolic activity was determined using the MTT assay. Data are means ± SD values from three experiments.
PC9ER cells were treated for 24 h with saline, vehicle (DMSO), the indicated TKIs (each at 10 nM), mAb565 (20 μg/ml) against EGFR, cetuximab (CTX; 20 μg/ml), and two different antibody mixtures (3×mAbs): murine (M; mAbs 565, N12 and mAb33; each at 20 μg/ml) and partly human (H; CTX, TRZ and mAb33; each at 20 μg/ml). Thereafter, cells were analyzed using flow cytometry for surface expression levels of EGFR, HER2, and HER3. Normalized data are means ± SEM of two independent experiments.
H1975 cells (3 × 106 cells per animal) were subcutaneously grafted in the flanks of CD1‐nu/nu mice, which were subsequently randomized and subjected to the following treatments: erlotinib (50 mg/kg/day), osimertinib (5 mg/kg/day), or 3×mAbs (CTX, TRZ, and mAb33; 0.2 mg/mouse/injection; administered twice a week). Shown is immunohistochemical staining for KI67 in paraffin‐embedded sections using specific antibodies. Scale bars, 100 μm.
CD1‐nu/nu mice harboring H1975 NSCLC xenografts were treated as indicated for 10 days. Thereafter, tumors were harvested, embedded in paraffin, and stained with antibodies specific to EGFR, EGFR‐L858R, and phospho‐EGFR (Y1068). Scale bars, 100 μm.
Comparison of body weights (averages ± SD) of groups of eight CD1‐nu/nu mice harboring H1975 xenografts and treated with either erlotinib (50 mg/kg/day), osimertinib (5 mg/kg/day), or a mixture of three mAbs (3×mAbs; CTX, TRZ, and mAb33; 0.2 mg/mouse/injection). Note that TKIs were daily administered using oral gavage, while the triple antibody combination was injected intraperitoneally once every 3 days.
PC9ER cells (3 × 106 cells per animal) were subcutaneously grafted in the flanks of CD1‐nu/nu mice. Animals were randomized into groups of six mice after tumors became palpable. Erlotinib (50 mg/kg/day) and osimertinib (5 mg/kg/day) were daily administered using oral gavage, while the triple antibody combination (3×mAbs; CTX, TRZ, and mAb33; 0.2 mg/mouse/injection) was administered intraperitoneally once every 3 days. Shown are results of body mass composition analyses (mean ± SD) of the fraction of fat mass (left) and lean mass (right) on day 20 of treatment. Mice harboring no tumors represent an internal control. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's test.